5 key facts about this project
### Overview
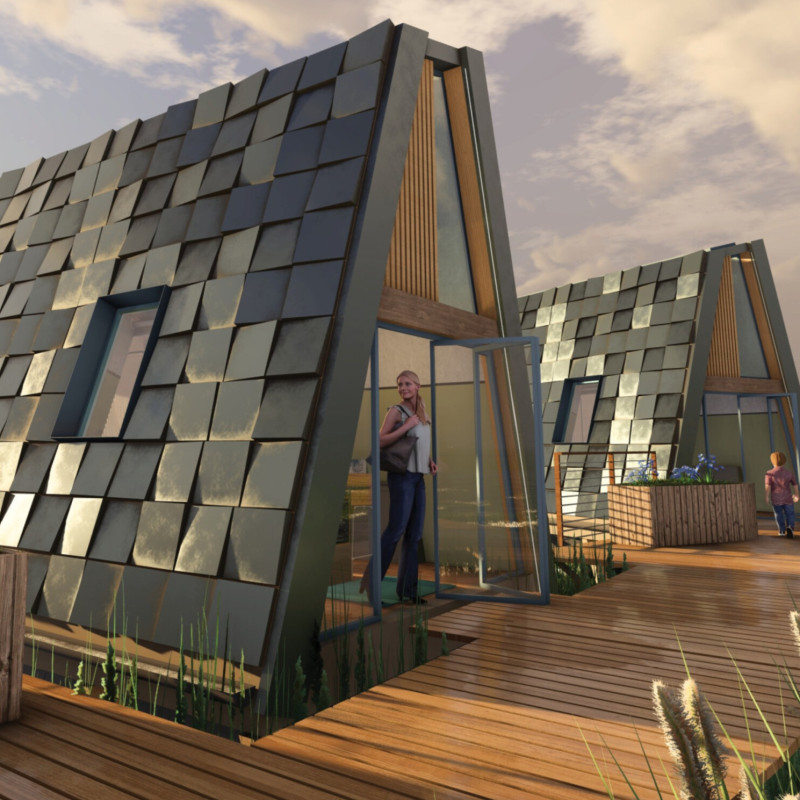
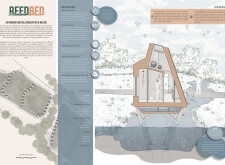
The ReedBed project, located in the United Kingdom, establishes a model for sustainable housing in response to urbanization and environmental challenges. It aims to minimize ecological impact while fostering a relationship between residents and nearby ecosystems. The design integrates dwellings with a constructed wetland system, enhancing biodiversity and promoting environmental stewardship alongside modern living amenities.
### Material Innovation
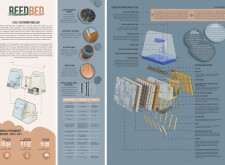
A focus on sustainable materials is integral to the project’s design. The tapered rainscreen cladding serves as the exterior layer, made from eco-friendly materials that contribute to both durability and aesthetic appeal. Walls are constructed using exposed OSB and structural insulated panels (SIPs) to enhance energy efficiency and thermal insulation. Water management is supported by metal tanks for rainwater collection and innovative greywater treatment systems, which promote circular water use. Additionally, naturally sourced timber flooring and high-efficiency thermally broken doors and windows further enhance indoor comfort and sustainability.
### Ecological and Community Integration
The project's architectural features include raised dwellings that minimize land impact and facilitate natural flood management. Public boardwalks connect homes to communal areas, promoting engagement and interaction within the community. A constructed wetland serves multiple ecological functions, enriching both the habitat and residents' daily experiences by providing educational and recreational opportunities. The incorporation of biophilic design principles fosters a living environment enriched with natural elements, enhancing residents' mental wellbeing and overall living quality.