5 key facts about this project
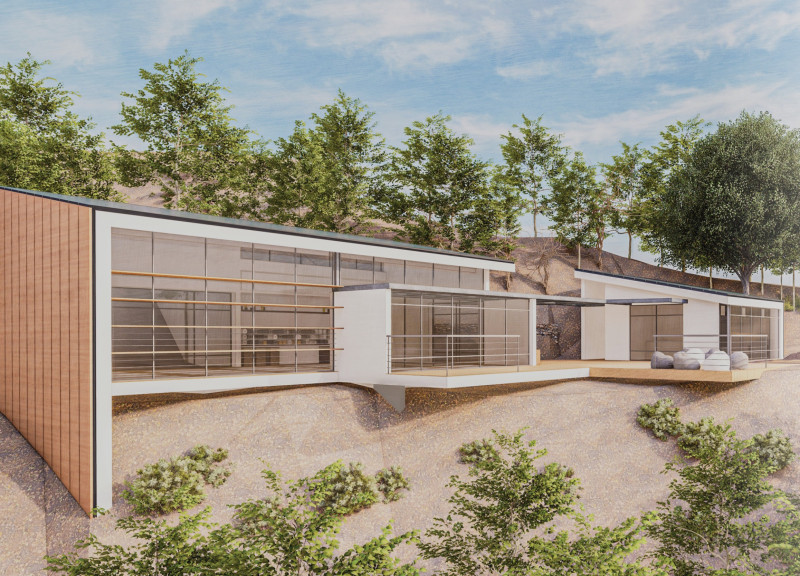
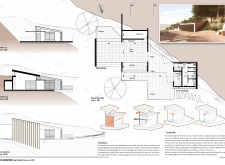
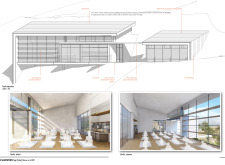
The Yoga Solar House is located in Vale de Moses Yoga Retreat in Portugal. It serves as a space for yoga practice while blending with the surrounding nature. The design focuses on sustainability and energy efficiency, with a concept centered around maximizing sunlight and reducing energy use. The structure provides an environment that encourages relaxation and mindfulness.
Orientation and Form
The building is strategically oriented to take advantage of the sun’s path. The main façade faces west, allowing significant winter sun exposure while offering shade from the hot summer sun. This thoughtful orientation enhances the comfort of users and employs passive heating strategies essential for maintaining energy performance.
Functional Zoning
The Yoga Solar House consists of two main volumes. The practice area is located to the west, while the service area, which includes the kitchen, showers, and toilets, is on the east. This clear division of functions helps organize the space effectively. Between these two volumes lies an outdoor terrace that serves as a social area, encouraging interaction among users and creating a sense of community.
Material Considerations
The project incorporates insulated clay block walls and a concrete ceiling. These materials are chosen for their structural strength and thermal mass. By selecting these options, the design supports durability and energy efficiency, optimizing the building’s performance. The material choices reflect a commitment to thoughtful and sustainable design.
Water Management Strategies
An important feature of the Yoga Solar House is its water management system. It uses a combination of rainwater and dew harvesting alongside a greywater recycling process. This design promotes resource use efficiency and aligns with ecological sustainability. Through these strategies, the building minimizes its environmental impact and utilizes local climatic conditions effectively.
The sloped roof of the Yoga Solar House follows the natural contours of the cliff. This design element not only integrates the building with its landscape but also harnesses solar energy for effective energy generation.