5 key facts about this project
## Overview
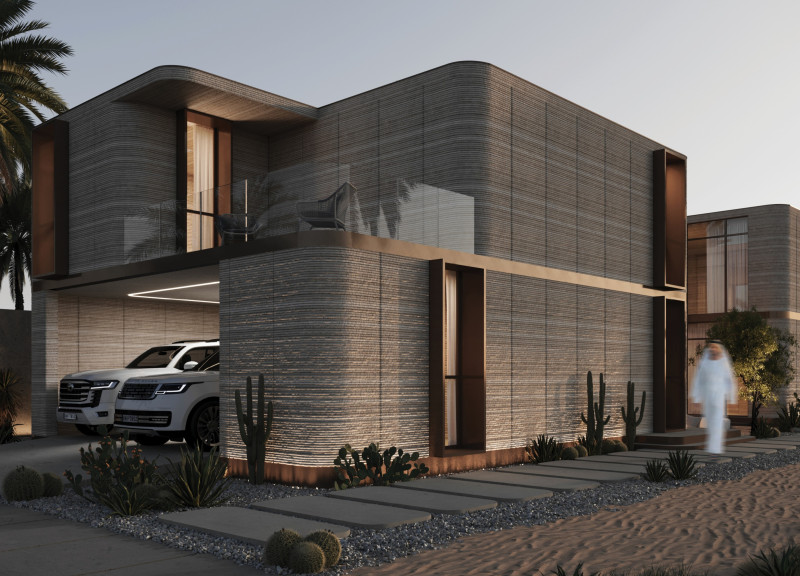
The design project located in Dubai merges traditional Emirati architectural elements with modern construction techniques. The intent is to create a residential environment that meets contemporary lifestyle needs while honoring the cultural heritage of the region. This approach facilitates a dynamic living space that emphasizes functionality and aesthetic coherence.
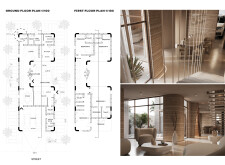
## Spatial Strategy
The architectural form is shaped through a systematic design process that prioritizes privacy and environmental integration. The building’s footprint is offset by 3 meters, allowing for landscaping that enhances both privacy and natural cooling. The incorporation of a central courtyard serves as a ventilation strategy essential in hot climates, while the rounded edges of the structure provide a welcoming aesthetic and improve airflow. Internal layout supports functionality, with an open-plan design that encourages social interaction while ensuring that private spaces remain accessible yet distinct.
## Materiality and Sustainability
Material selection is foundational to the project's sustainability goals. The use of 3D-printed walls and columns, constructed from local materials, provides flexibility tailored to occupant needs and reduces construction waste. Local clay is employed for its natural humidity absorption and thermal resistance. Additionally, the building features a solar panel system and an atmospheric water generation system that collect moisture from the air. These sustainable practices are further complemented by traditional windcatchers, which enhance natural ventilation, thereby lowering energy consumption. The project is designed for adaptability, allowing for future expansion in alignment with occupant requirements.