5 key facts about this project
## Overview
The Nordic Pavilion, situated in the Krafla Ski area of Norðurland eystra, Iceland, is designed for the Iceland Snow Cabin Architecture Competition. This project prioritizes a harmonious integration with the natural landscape, with an emphasis on sustainability, functionality, and aesthetic simplicity.
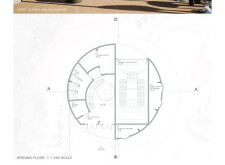
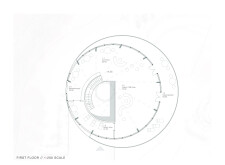
## Spatial Configuration
The pavilion's design features a circular structure that facilitates an engaging interaction between visitors and the surrounding scenery. The layout includes numerous windows and a prominent skylight to maximize natural light and provide unobstructed vistas of the landscape. A spacious viewing deck encircles the entrance, offering nearly 360-degree views of the local mountains and lava plains, enhancing the user experience by connecting interior spaces with the exterior environment.
## Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability is central to the design philosophy of the Nordic Pavilion. Sustainable materials were sourced locally, minimizing environmental impact. The incorporation of geothermal heating takes advantage of the site's natural resources, while strategically placed solar panels provide renewable energy to meet the pavilion's power requirements. An innovative water management system, designed to emulate local natural springs, promotes efficient water usage and supports the building's ecological objectives. These elements illustrate a commitment to responsible design within fragile ecosystems.