5 key facts about this project
### Overview
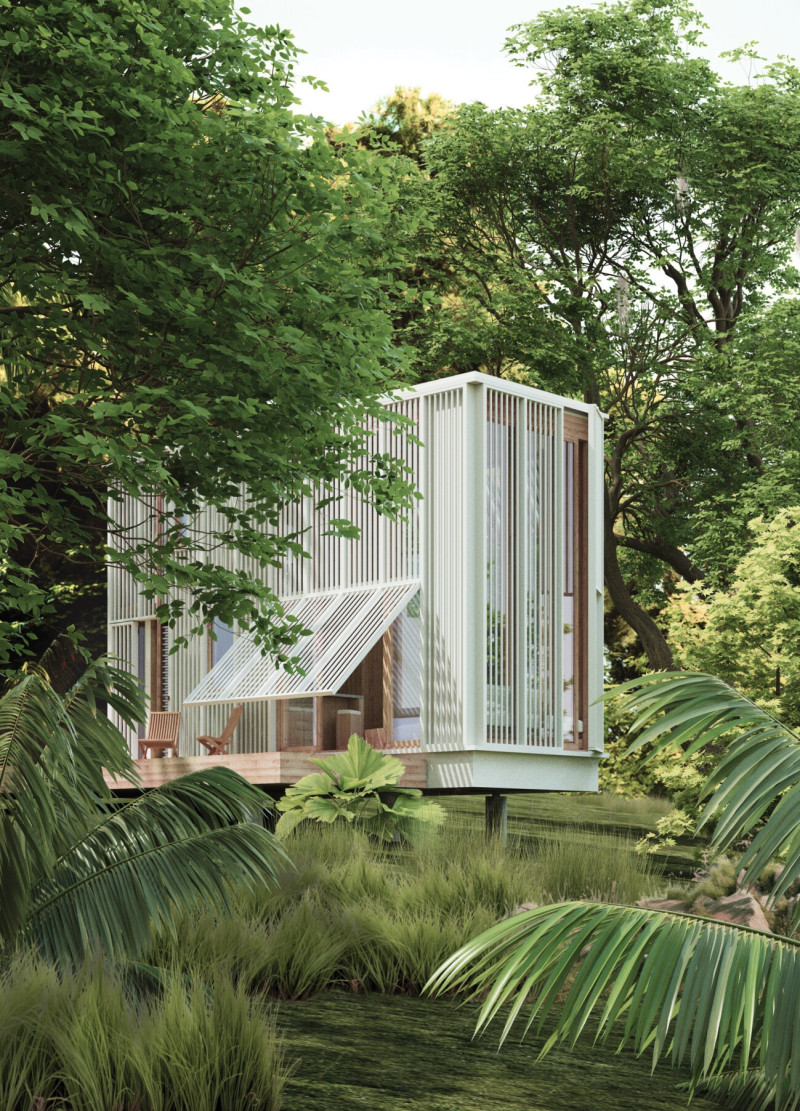
Located within a rich subtropical landscape, the Egret project focuses on sustainable living through innovative architectural design. This housing prototype emphasizes micro-living and eco-friendly principles, aiming to create a harmonious relationship between residents and their natural environment. By prioritizing minimal land impact and climate adaptability, the design fosters a community-oriented atmosphere that encourages interaction and shared spaces.
### Site Context and Environmental Integration
The Egret home is thoughtfully elevated on stilts to preserve the surrounding ecosystem and minimize ecological disruption. This elevation not only provides enhanced views of the lush greenery and diverse flora but also allows the ground to remain undisturbed, supporting local wildlife. The layout is designed to integrate with the vibrant subtropical environment, creating a structure that complements its natural context.
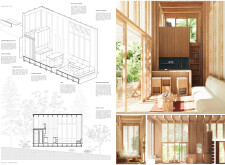
### Spatial Organization and Functionality
The interior layout is centered around an open-plan living area that promotes communal activities by linking the kitchen and dining spaces. Flexibility is a key aspect of the design, with convertible spaces achieved through movable partitions and multi-purpose furniture, such as a lofted sleeping area. Passive cooling strategies, including operable windows and thermal mass, optimize the interior climate without relying on mechanical cooling.
### Material Selection and Sustainability
The project employs a carefully selected combination of materials to enhance both ecological performance and aesthetic appeal. Wooden elements provide warmth and comfort, while aluminum frames and vertical louvered screens ensure durability and effective shading. Expanses of glass facilitate a connection to the outdoors and are strategically positioned to manage solar gain. Concrete is utilized for stability and structural support, establishing a robust foundation. Sustainable features, such as rainwater harvesting systems and landscaping with native plant species, contribute to reduced resource consumption and promote biodiversity.