5 key facts about this project
### Analytical Report on the Architectural Design Project: Ármadar / Shelter
#### Overview
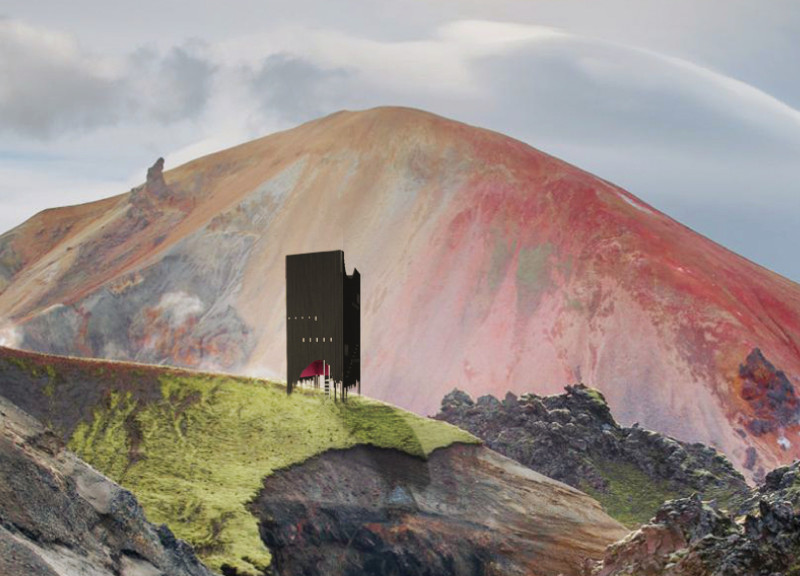
Ármadar, located within the dramatic landscape of Iceland, focuses on modern conceptualizations of shelter, drawing inspiration from the region's unique topography and cultural narratives. The project's intent is to create a refuge for outdoor adventurers, fostering a deeper connection between users and their surrounding environment. This structure serves as both a practical resting point for trekkers navigating Iceland's rugged terrain and a representation of local folklore, encapsulating stories of human interaction with nature.
#### Structural Composition and Materiality
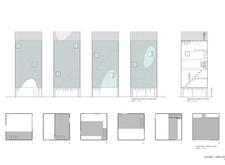
The design features an angular silhouette that appears to emerge from the landscape, integrating seamlessly with its surroundings. The exterior is clad in vertical wooden slats, offering a textured facade that harmonizes with the natural elements. A striking arched entryway incorporates irregular cutouts, inviting occupants to engage with sweeping views outside.
The material selection emphasizes durability and efficiency, utilizing 2x4 timber for the structural framework and 4x8 plywood for internal and external envelopes, ensuring thermal insulation. Photovoltaic panel pavers on the roof provide sustainable energy, underscoring the project's emphasis on self-sufficiency. The juxtaposition of dark, charred timber with lighter plywood further balances the rugged exterior with inviting interior spaces.
#### Spatial Configuration and Sustainability
The interior layout is designed for multifunctionality, providing areas for sleeping, gathering, and observation. Various sleeping levels are incorporated, creating distinct intimate spaces that enhance user experience while allowing natural light and ventilation to permeate throughout the structure. Strategic viewing platforms enable occupants to appreciate the panoramic landscape, enriching their connection to the environment.
Sustainability is paramount in this design, integrating water collection systems and elevating the structure on piers to mitigate erosion and preserve vegetation. This approach exemplifies a commitment to environmental sensitivity and a seamless integration with the surrounding ecosystem, establishing a responsible framework for future architectural endeavors in similar contexts.