5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
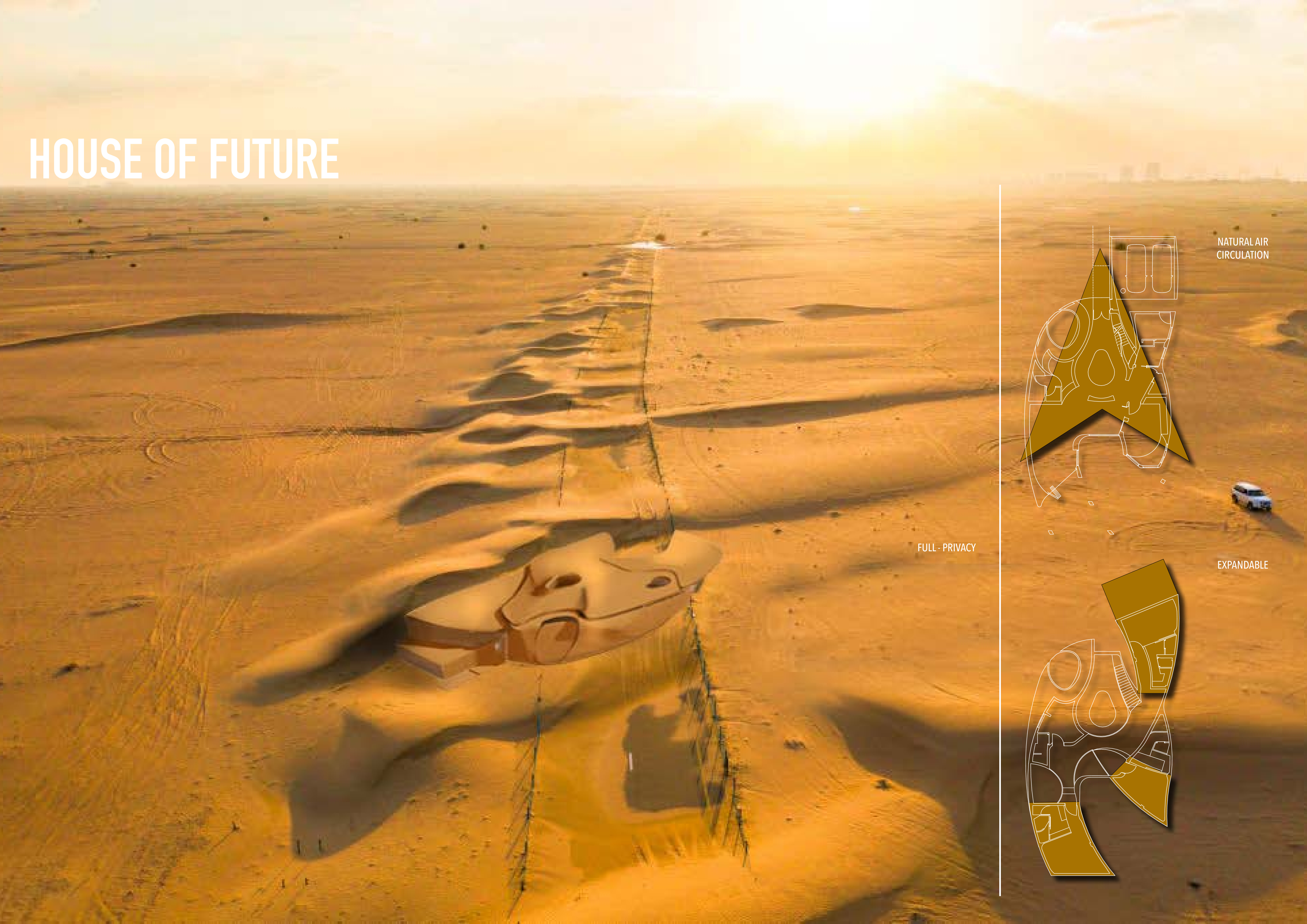
Located in a desert environment, the House of the Future combines modern architectural practices with sustainable design principles. The proposal integrates traditional elements with advanced ecological technologies, aiming to create a harmonious relationship between habitation and the natural landscape.
## Climate-Responsive Design
The design prioritizes adaptability and the incorporation of natural elements, facilitating a climate-responsive strategy. The structure's form is inspired by natural outcroppings to enhance its compatibility with the surrounding terrain. Different functional zones, such as living areas, private spaces, and utility sections, are strategically arranged to promote efficient circulation and interaction among occupants.
### Material Selection
Materiality plays a critical role in achieving both sustainability and aesthetic appeal. The use of reinforced concrete provides structural durability and thermal mass, while strategically placed glass elements maximize natural light and offer views of the desert landscape. Additionally, the selection of wood finishes adds warmth and texture, balancing the starkness of the concrete. Consideration for sustainability is reflected in the proposed use of recycled and locally sourced materials, minimizing the overall carbon footprint of the project.
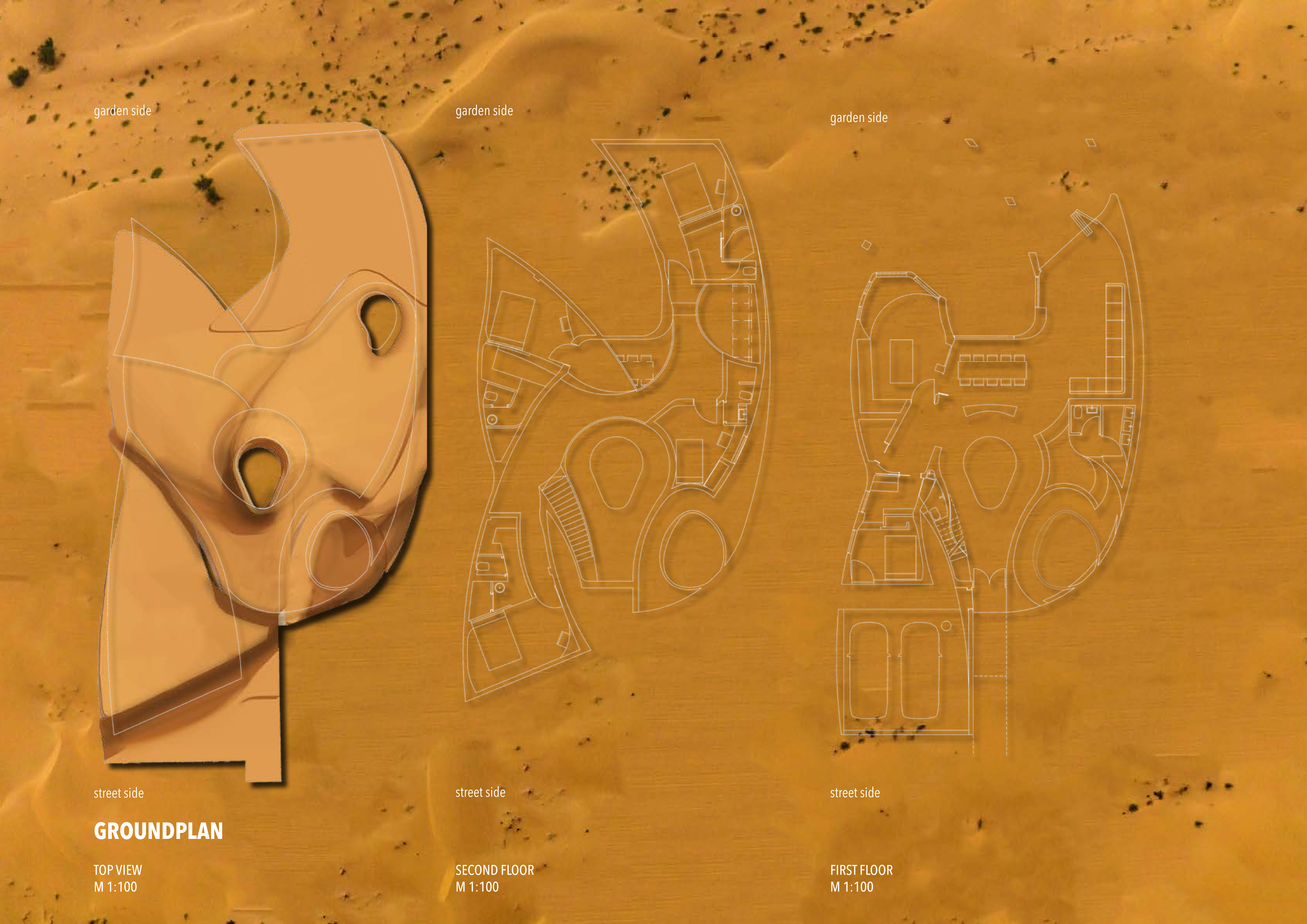
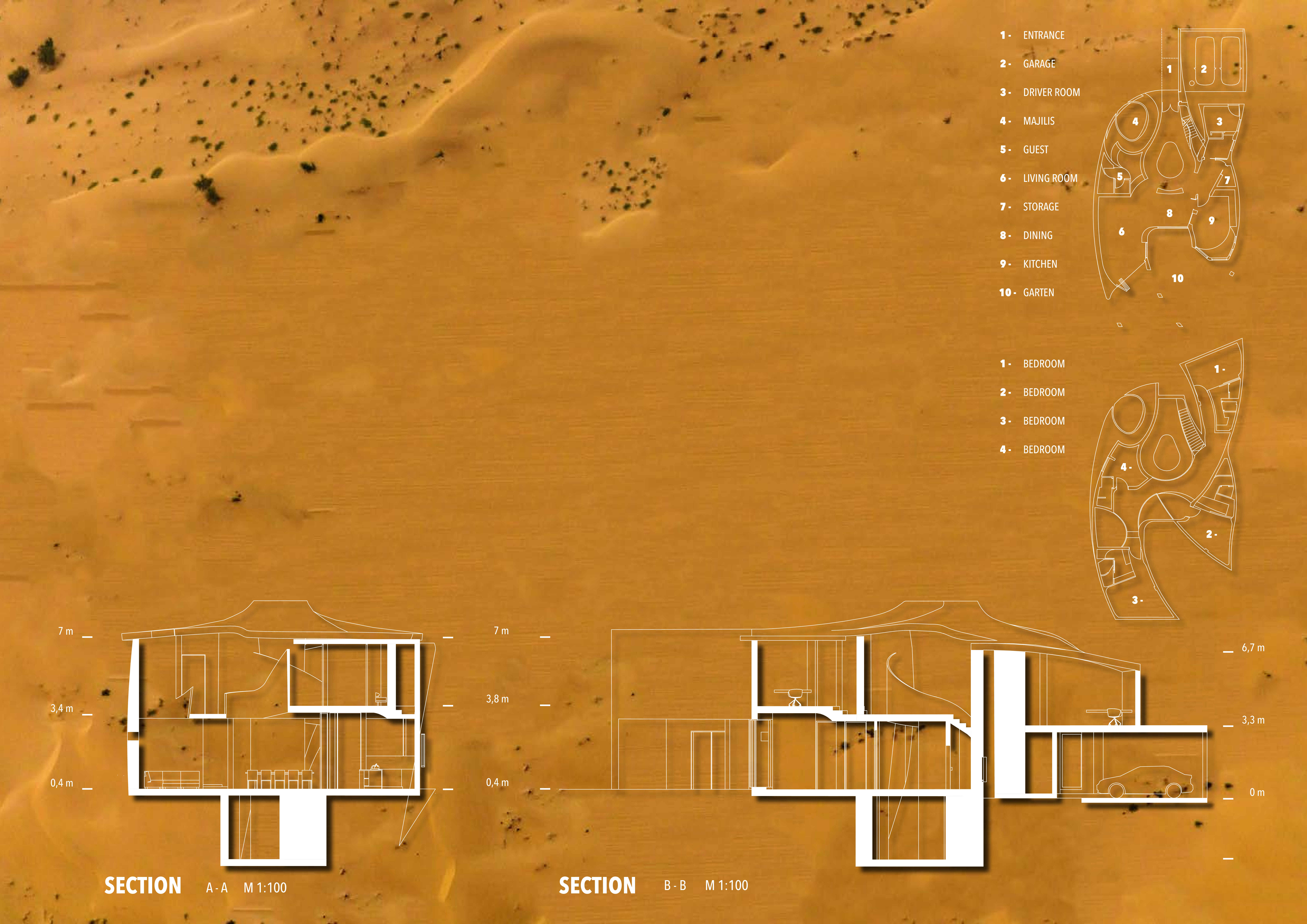
## Functional Layout
The internal organization of the space is designed to accommodate both communal and private interactions. The first floor features open living areas, a dining space, and a kitchen, fostering social engagement, while the second floor is reserved for private quarters. Thoughtful circulation paths are established to encourage movement throughout the structure, with outdoor gardens integrated into the design to amplify the connection with nature.
### Sustainable Systems
The implementation of sustainable systems is a key aspect of the design. Rainwater collection systems are proposed to capture and recycle water for landscape irrigation and potential internal use, addressing water resource challenges in arid regions. Additionally, the roof is designed to accommodate solar panels, enabling energy generation that can support the operation of the entire dwelling.