5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
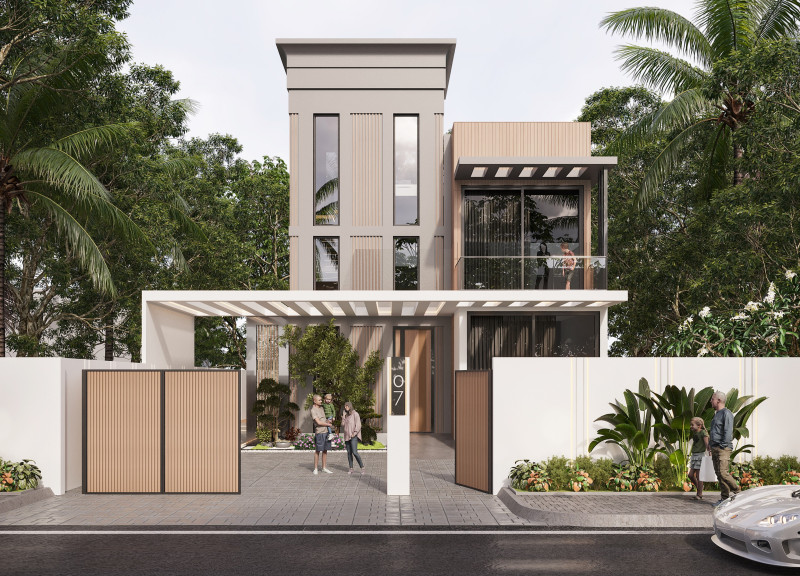
Located in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the House of the Future is designed to provide a sustainable and innovative housing solution that reflects the cultural and climatic context of the region. The project integrates contemporary architectural practices with an emphasis on sustainability and user-centered design, aiming to enhance the living experience while fostering a connection to the local environment.
### Architectural Philosophy and Spatial Flexibility
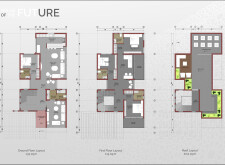
The design philosophy prioritizes a strong connection between occupants and their surroundings through the application of biophilic design principles. This approach enhances resident well-being by incorporating natural elements into the living space. Additionally, a user-centric strategy ensures that the functional and comfort needs of residents are met. The spatial design features modularity and adaptability, allowing the dwelling to evolve alongside the changing requirements of its inhabitants, thus promoting a dynamic living environment.
### Material Selection and Energy Efficiency
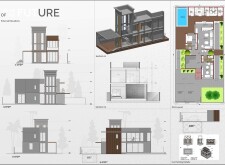
Sustainability is a cornerstone of the material choices, which include recycled materials and natural finishes that reflect the landscape of Dubai. Key components, such as graffiti-textured paint and wooden slat cladding, are carefully selected to enhance aesthetic appeal while ensuring resource conservation. Energy efficiency is addressed through passive solar design, optimal window placement for natural daylight, and the integration of renewable energy sources, including solar panels and potential wind turbines. Water efficiency measures, such as rainwater harvesting systems and water-conserving fixtures, further align the design with sustainable practices.
### Accessibility and Landscape Integration
The project adheres to universal design principles, ensuring accessibility for all individuals and promoting inclusivity. The landscape design incorporates native, drought-resistant plants that enhance biodiversity and reduce irrigation needs. Durable construction techniques and materials have been employed to minimize maintenance requirements, contributing to long-term sustainability while harmonizing with the built and natural environment. Notable architectural features, including graft-textured facades and multi-functional interior spaces, enhance both aesthetic richness and utility.