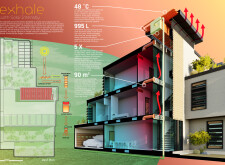
5 key facts about this project
### Overview
Located in a climate-sensitive environment, the AZIMUTH project emphasizes sustainable residential architecture with an intent to foster a cohesive community structure. The design is informed by local climatic conditions, integrating both environmental and social factors into the living spaces, thereby promoting energy efficiency and ecological responsibility.
### Spatial Strategy and Community Interaction
The layout consists of a series of interconnected residential units that facilitate social interaction among residents. Central to the design are several key architectural features, including a Heat Stack Tower that enhances thermal regulation through natural ventilation, and a Wind Catcher that optimizes airflow, reducing dependency on mechanical cooling systems. Additionally, xeriscape roof gardens serve both aesthetic and functional purposes, contributing to water management and biodiversity, while providing spaces for food cultivation.
### Material and Technological Integration
The project employs a selection of materials carefully chosen for their performance characteristics. Acoustic and insulating panels in the walls enhance thermal efficiency, complemented by solar collectors and retention tanks that maximize solar energy capture. The exterior features 3D printed composites, presenting a modern interpretation of traditional architectural elements while upholding sustainability. The incorporation of smart water systems and photovoltaic panels demonstrates a commitment to energy management and resource conservation, significantly lessening the environmental impact of the development.