5 key facts about this project
# EcuLiving Lab: Architectural Analysis Report
## Overview
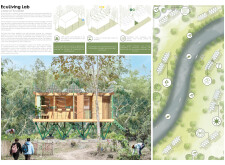
EcuLiving Lab is situated on the Ecuadorian coast, designed specifically to address critical challenges faced by vulnerable communities, including climate change, community resilience, and food security. The project aims to provide sustainable housing solutions in areas at risk of natural disasters, sea-level rise, and food insecurity.
## Architectural Features
### Elevated Structure and Flexible Design
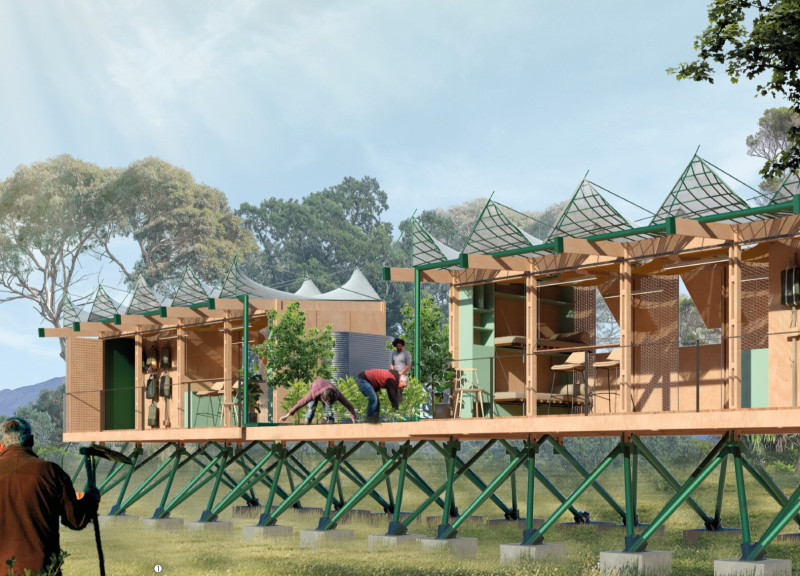
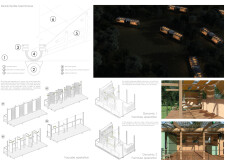
The design consists of multiple individual housing units elevated on a lightweight structural frame to minimize interaction with the natural ground. This elevated construction protects the homes from flooding and enhances environmental adaptability. The gabled roofs are designed to maximize natural light and ventilation, contributing to reduced reliance on artificial lighting and cooling systems. Interior spaces are adaptable, allowing for various configurations to meet changing user needs for living, cooking, working, and social engagement.
### Sustainable Materiality
EcuLiving Lab utilizes a selection of materials that emphasize sustainability and performance. TEKA wood, known for its durability and resistance to moisture, is the primary structural material. Prefabricated metal elements enhance structural integrity while maintaining a lightweight profile. A textile membrane adds aesthetic value while regulating solar exposure, and perforated panels provide natural ventilation and privacy without sacrificing views of the landscape. The incorporation of rainwater harvesting systems is a crucial feature, allowing for water collection and storage to enhance self-sufficiency.
## Community-Centered Design
Shared gardens are strategically placed between housing units to foster community interaction and promote ecological practices. These gardens not only allow residents to grow organic produce but also contribute to food sovereignty, particularly during drought conditions. The emphasis on collective living supports social cohesion and active participation among residents.
## Bioclimatic Strategies
The project implements various bioclimatic strategies to optimize resource use. The layout facilitates natural ventilation, minimizing reliance on mechanical climate control. Structures are oriented to maximize sunlight exposure during the day, while shaded areas maintain comfortable outdoor environments. The design integrates natural resource utilization through rainwater harvesting and sustainable agricultural practices, thereby reducing the ecological footprint of residents.
Through these design elements, EcuLiving Lab aims to provide an immediate response to housing needs while also addressing broader environmental and social challenges faced by coastal communities.