5 key facts about this project
### Overview
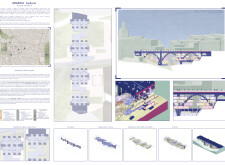
ARCADIA habitat is located in Madrid, Spain, designed as a response to the city's pressing need for affordable housing. Aiming to revitalize the urban landscape, the project seeks to integrate diverse communities through innovative architectural solutions that align with the cultural and historical context of the area. The initiative addresses both environmental concerns and social challenges associated with urbanization by focusing on creating living spaces that foster community engagement and inclusivity.
### Spatial Organization
The architectural layout features a series of interconnected residential units designed for flexibility and adaptability to accommodate various household structures. The modular approach combines communal and private spaces, effectively catering to families, students, and individuals. The design incorporates multiple circulation paths that facilitate ease of movement and encourage social interactions among residents. Additionally, strategically positioned terraces and shared communal areas serve as gathering spots, reinforcing the project's commitment to fostering connections within a diverse community.
### Material Selection
The material choices underscore a commitment to sustainability and resilience. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) serves as the primary structural component, offering strength while encapsulating carbon throughout its lifecycle. Recycled concrete reduces waste and the carbon footprint associated with traditional concrete production. Ample use of glass for windows ensures maximum natural light and energy efficiency, while caloric insulation optimizes energy use within the units. Integration of solar panels contributes to the project's goal of energy self-sufficiency, further aligning with sustainable design principles.