5 key facts about this project
### Overview
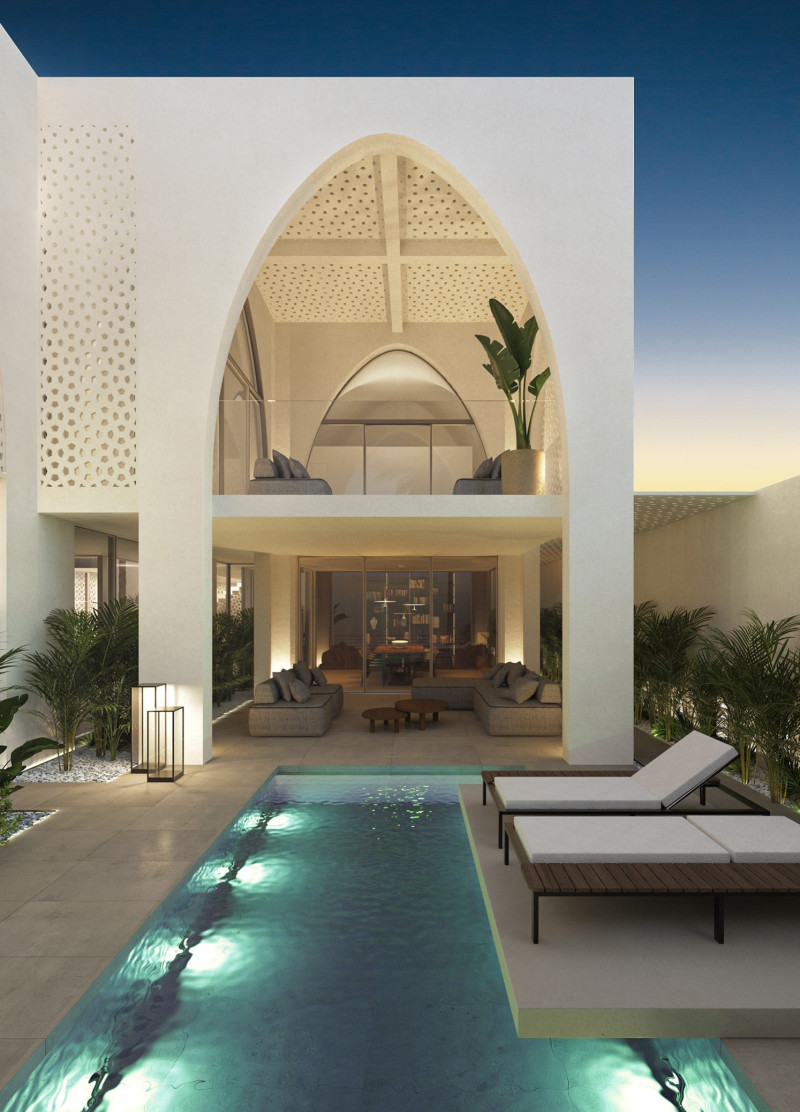
The architectural design for New Roots is set in the United Arab Emirates, reflecting a contemporary vision of residential living that integrates cultural heritage with modern innovations. The intent is to create a sustainable living environment that addresses the current and future needs of the community while respecting the local context. Key design principles center around modularity, environmental sustainability, and cultural resonance.
### Spatial Organization
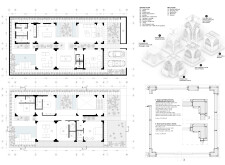
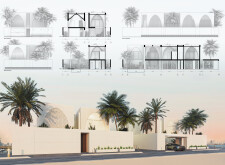
The spatial strategy incorporates a thoughtful layout, wherein communal areas on the ground floor—such as the living room and dining space—foster social interaction, while private spaces are allocated to the upper levels. Large windows and strategically placed open-air courtyards allow for the infiltration of natural light and facilitate cross-ventilation, enhancing the overall spatial experience. The modular design promotes flexibility, allowing for future expansions as needed.
### Material Selection
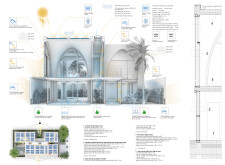
Materials utilized in the construction emphasize both sustainability and functionality. Prefabricated concrete forms the structural backbone, enabling efficient site assembly. The facade features 3D-printed ceramic tiles that reflect traditional designs, offering a connection to cultural heritage through contemporary methods. A substantial glass façade provides natural illumination and views of exterior landscapes, while strategically placed wood elements contribute warmth and texture throughout the interiors, improving spatial comfort.
### Innovative Features
New Roots incorporates a comprehensive photovoltaic system consisting of 52 solar panels, generating approximately 37,944 kWh annually, which underscores the commitment to energy autonomy. Water management systems, including rainwater harvesting and a storage capacity of 500 liters, support efficient resource use. Additionally, the design features passive cooling and ventilation mechanisms, utilizing operable grilles and water bodies to enhance thermal comfort while reducing dependence on mechanical systems.