5 key facts about this project
**General Overview**
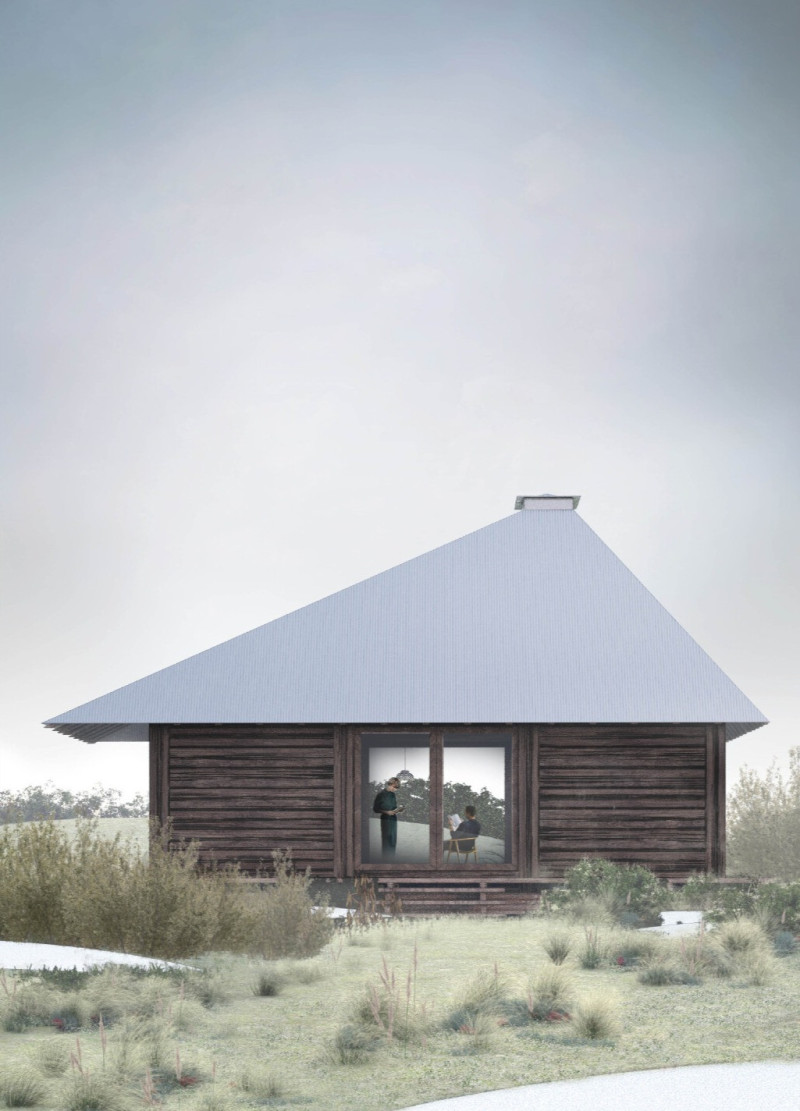
Located in a polar region significantly affected by climate change, the Arctic Cabin exemplifies an architectural response to urgent environmental challenges. The project's intent focuses on fostering a sustainable relationship between inhabitants and their surroundings, emphasizing material reuse, ecological adaptability, and minimizing environmental impact. It highlights a commitment to reconnecting individuals with the natural landscape while addressing the vulnerabilities of the Arctic ecosystem.
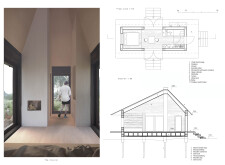
**Architectural Form and Spatial Configuration**
The design features a steeply pitched roof that facilitates snow retention, effectively enhancing insulation within the cabin while addressing the needs of the Arctic climate. Elevated on pilings, the structure minimizes disruption to the delicate ground below, reflecting a commitment to environmental stewardship. The compact floor plan is designed for multifunctionality, incorporating essential spaces such as a living area centered around a fireplace, an efficiently integrated kitchenette, and cozy sleeping quarters. This layout promotes communal engagement while optimizing the use of space.
**Material Selection and Sustainability**
The materials chosen for construction underscore a focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility. Structural elements utilize massive timber logs, acknowledging wood's renewable nature, while wood paneling enhances both insulation and aesthetic appeal. The durable steel roof is designed to withstand harsh weather, and the wooden slab foundation provides stability with minimal ecological impact. Each material was selected not only for its functional benefits but also for its capacity for future disassembly and reuse, aligning with the project's overarching sustainability goals.
**Innovative Adaptability Features**
The design incorporates a modular approach that supports adaptability, allowing for various configurations of living units that can accommodate small communities while ensuring privacy. This flexibility enhances communal living and encourages architectural diversity within the Arctic context. Key design innovations include screw-down foundations and flexible joint systems that facilitate easy assembly and disassembly, minimizing environmental disturbance. Integrated systems promote self-sufficiency, such as rainwater collection, solar-powered heating, and composting toilets, fostering sustainable practices and encouraging food cultivation through productive gardens within the project.