5 key facts about this project
# Analytical Report on the "House of the Future" Architectural Design Project
## Overview
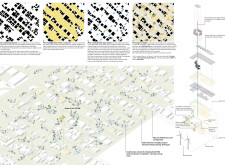
Situated in Al Qouz, a residential area in Dubai, UAE, the project explores the interplay between cultural identity, sustainability, and urban community living. The design integrates traditional forms with modern methodologies, creating a functional living space that responds to its environmental context. The intent is to address contemporary challenges in residential architecture while fostering community cohesion and individual expression.
## Spatial Strategy
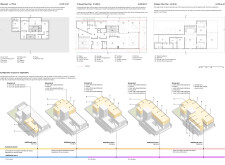
The site is strategically organized in a rectangular composition of 30x15 meters, featuring a basement and two levels that accommodate diverse functions while maintaining an aesthetically coherent form. The layout promotes interaction within the surrounding residential landscape, facilitating both individuality and a shared community identity. This approach is informed by a thorough understanding of the Al Qouz urban context, ensuring compatibility with local infrastructure and traditional elements, thus bridging past and present architectural narratives.
### Adaptable Spaces
The design incorporates flexibility, proposing various configurations to meet the evolving needs of its residents. Features such as open-plan areas and movable partitions enhance the utility of spaces, allowing for adjustments based on occupancy and use. This adaptability extends the residence's functionality over time, catering to changing lifestyles and preferences.
## Materiality and Sustainability
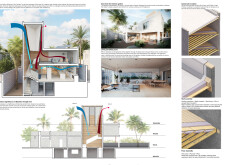
The material selection reflects a commitment to sustainability and cultural authenticity. Key materials include concrete for structural support, natural timber for warmth and versatility, and traditional lattice-work elements that facilitate ventilation while linking the design to regional heritage. Large glass windows are strategically placed to maximize natural light and connect residents with the surrounding gardens.
### Passive Cooling Systems
The integration of the "Barjeel," or wind tower, exemplifies the project's focus on passive cooling techniques. This architectural feature channels breezes into the house, minimizing reliance on mechanical cooling systems and reducing energy consumption. Additionally, the design incorporates a central garden that enhances biodiversity and water conservation through innovative landscaping strategies.
## Future Sustainability Initiatives
Beyond the immediate architectural design, the project aims to inform broader urban development strategies that emphasize renewable energy and resource management. Features such as solar panels on the roof and integrated waste treatment systems highlight a proactive approach to sustainability. These elements not only elevate the residence's ecological performance but also position it as a model for future residential developments in urban settings.