5 key facts about this project
### Overview
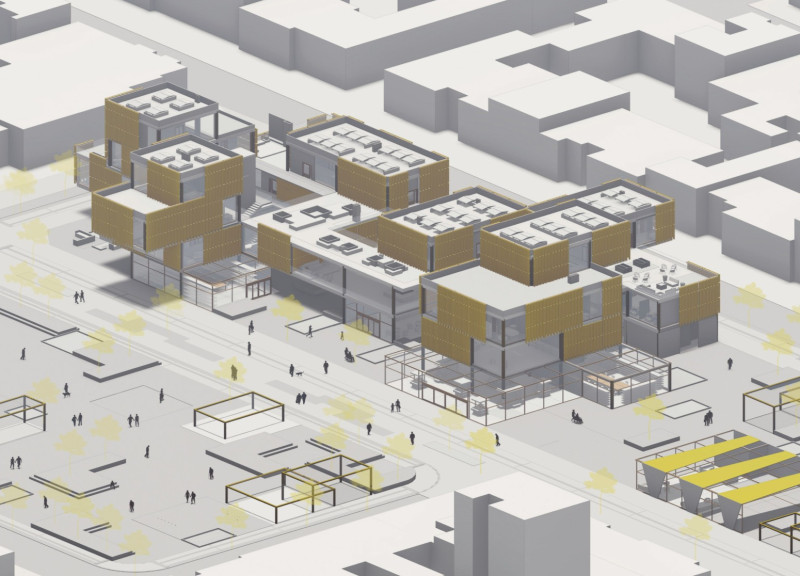
HiveHub is located in the urban center of Bogotá, Colombia, and is designed to address social isolation among the senior population. By embodying the structure and communal attributes of a beehive, the project aims to foster community interaction, adaptability, and environmental harmony. The architectural analysis will explore the design's conceptual framework, material selections, and spatial organization, highlighting its focus on fostering social connections and sustainability.
### Community-Centric Design
The design of HiveHub emphasizes community interaction through the arrangement of living spaces, conceived as individual modules or "cells." This layout promotes a sense of belonging while facilitating social engagement among residents. Core principles guiding the project include a commitment to sustainability through environmentally responsible materials and energy-efficient systems, and adaptability, allowing spaces to evolve with the changing needs of the community.
The strategic site selection enhances accessibility to vital services like healthcare and recreation, creating a living environment integrated with the urban landscape. Public spaces are a focal point in the layout, serving as communal hubs for leisure and interaction, thereby enriching the overall residential experience.
### Materiality and Sustainability
HiveHub's construction employs environmentally sustainable materials that ensure durability and aesthetic quality. Key materials used in the project include prefabricated metal modules for efficient assembly, concrete for structural integrity, and glass to promote natural light within living spaces. The integration of green terraces not only enhances the visual appeal but also contributes to environmental sustainability by supporting urban vegetation and biodiversity. Renewable energy is harnessed through the use of solar panels, while wood finishes create inviting interior environments.
### Spatial Organization
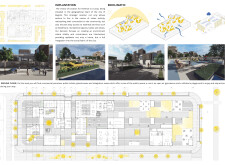
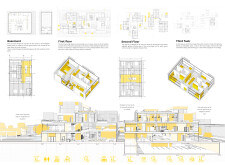
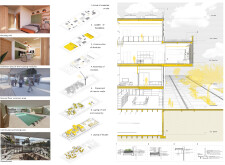
The ground floor is designed as a dynamic interface where public and residential areas converge, incorporating commercial spaces, greenhouses, and recreational facilities. Key features include an open-air gymnasium, playgrounds, and social gathering areas, ensuring that residents have easy access to both leisure and essential services without extensive travel.
Vertical organization is evident in the multi-story design, with each floor serving distinct functions. The first floor accommodates up to 32 residents with shared amenities including dining and recreational spaces. The second floor contains residential units with direct access to communal terraces, promoting outdoor engagement, while the third floor offers larger duplex apartments, providing comfort and high vantage points, complemented by dedicated community spaces that encourage user interaction.
### Bioclimatic Innovation
The design incorporates bioclimatic strategies to maximize energy efficiency, minimize operational costs, and support ecological principles. Natural light is harnessed through strategically positioned windows and glass interfaces, while cross-ventilation systems reduce reliance on mechanical cooling. Green roofs serve dual purposes as insulation for the structure and as communal gardening areas for residents.