5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
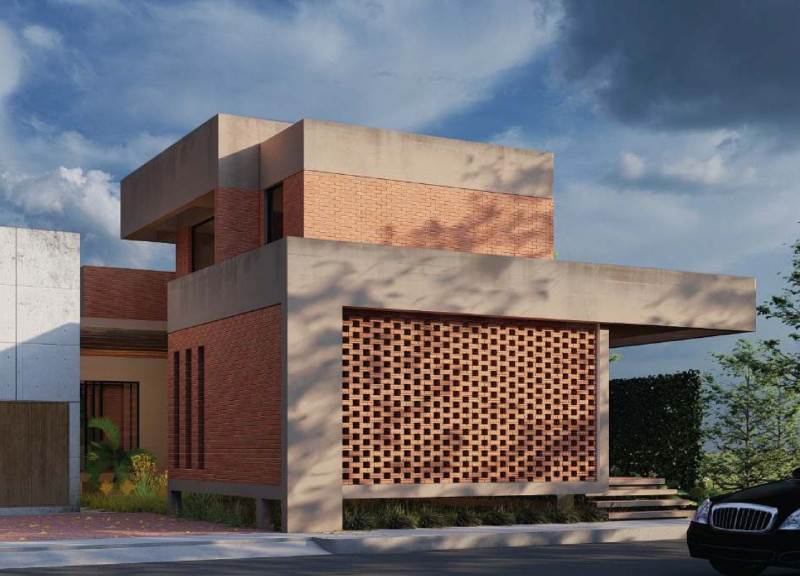
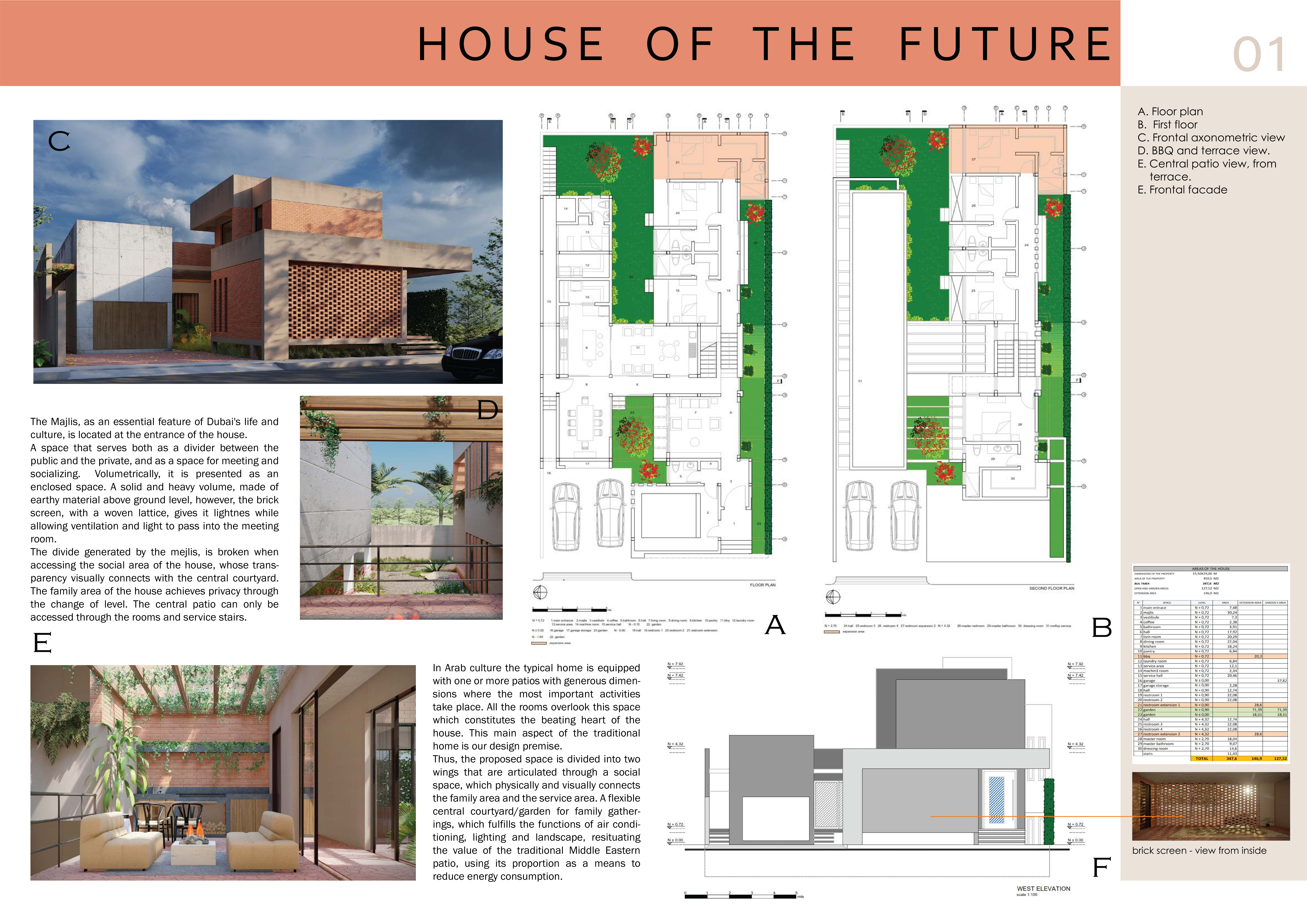
The House of the Future in Dubai is designed as a contemporary response to the traditional residential spaces of the region. It merges modern design elements with local cultural heritage, prioritizing sustainability and community engagement. The integration of advanced materials and technologies serves to enhance both the functionality and aesthetic coherence of the structure.
### Spatial Organization and Connectivity
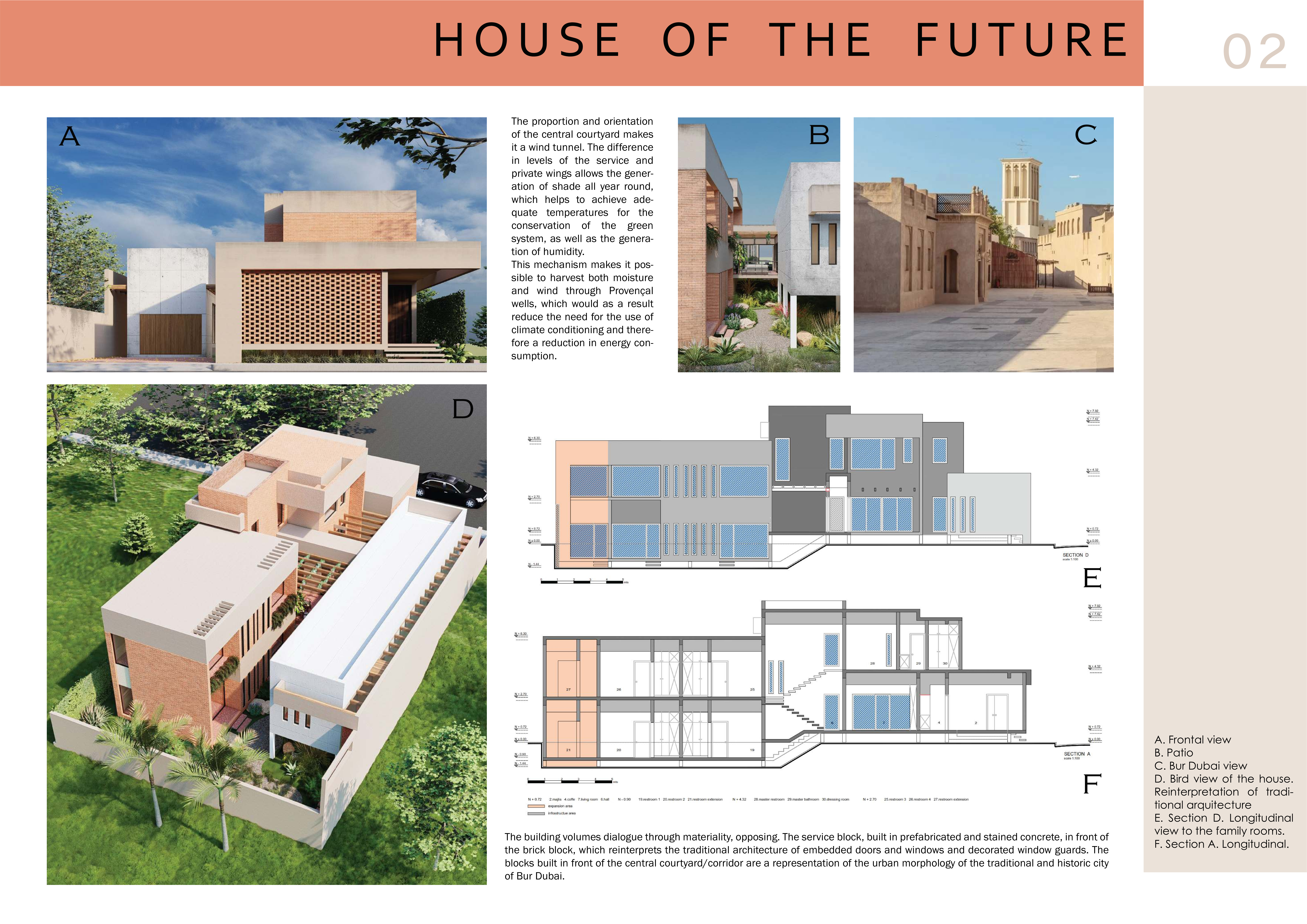
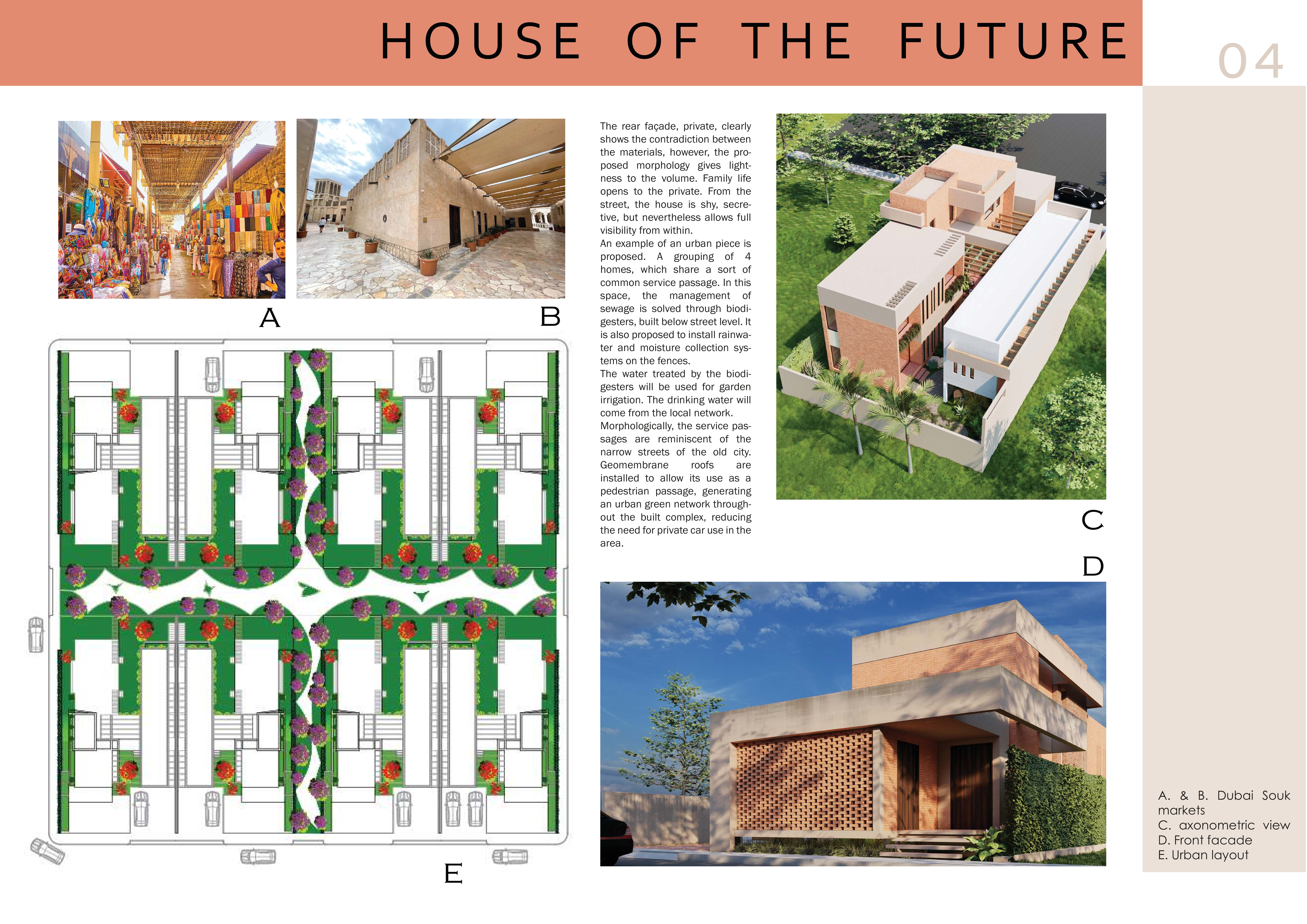
The design emphasizes the concept of the Majlis, a traditional gathering area central to social interaction in Middle Eastern culture. The layout features two distinct wings connected by a central courtyard, which facilitates natural ventilation and light while promoting communal and private interactions. Key areas, including the Majlis positioned at the entrance and designated family spaces organized around the courtyard, are purposefully arranged to create a harmonious balance between public and private realms.
### Material Selection and Environmental Focus
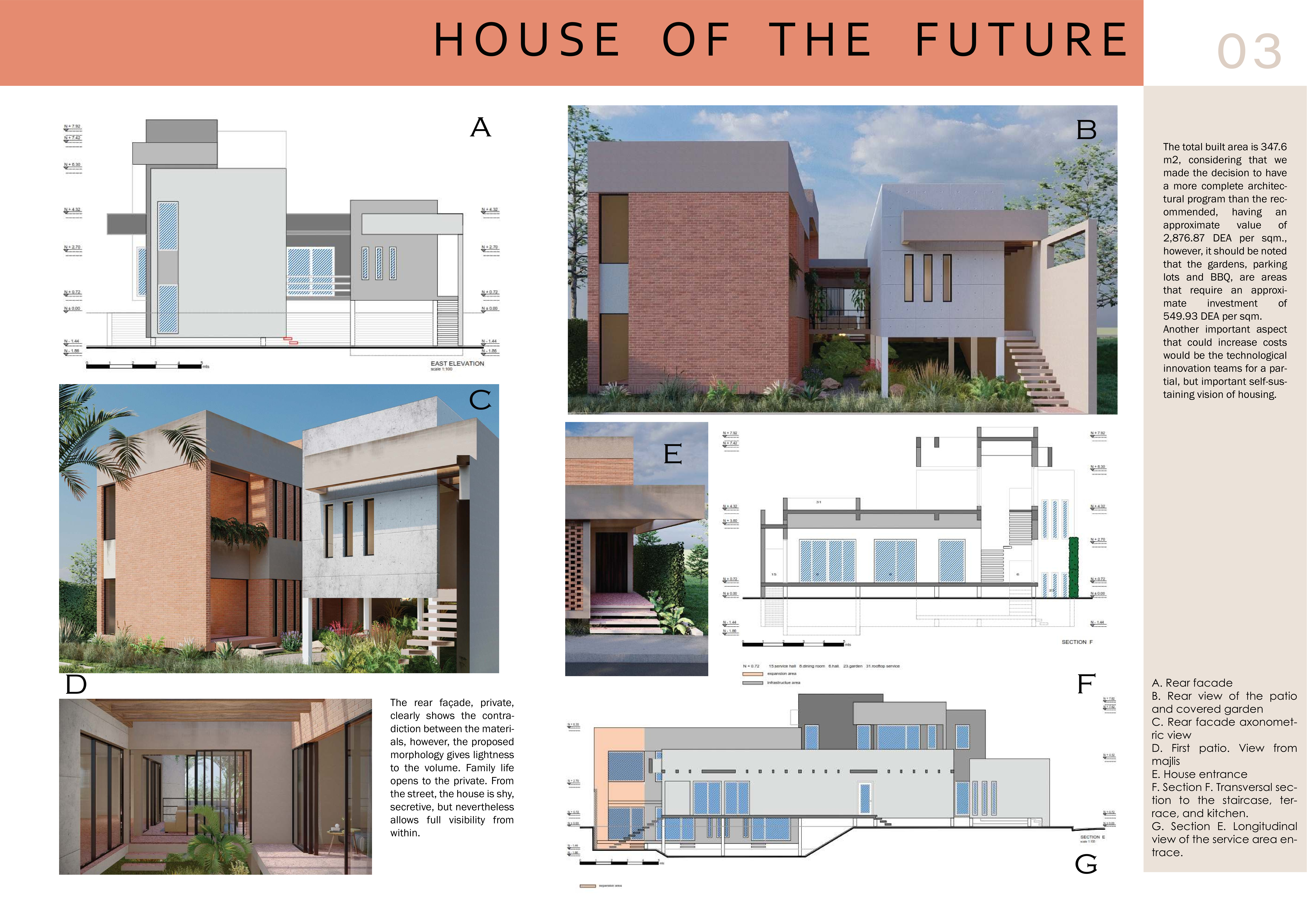
A deliberate choice of materials underpins the project’s sustainability goals. The use of locally sourced brick contributes to structural integrity and aesthetic resonance with traditional architecture. Prefabricated concrete provides durability and accommodates modern finishes, while extensive glazing enhances transparency, allowing for abundant natural light. Green wall systems and bio-digesters are incorporated to effectively manage temperature and humidity, aligning with sensitive ecological practices relevant to Dubai's urban context.