5 key facts about this project
## Overview
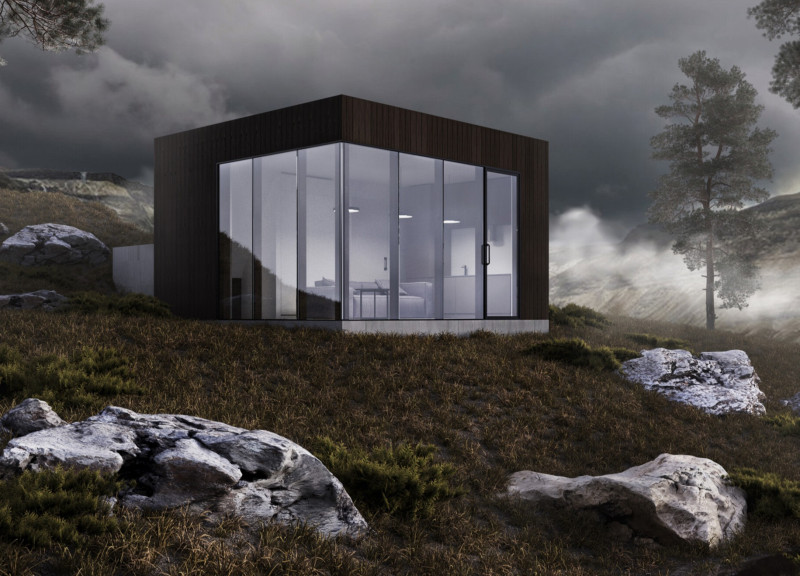
The Bunker House is a response to the socio-political challenges in Ukraine, specifically designed to provide safe and functional microhousing in areas affected by military conflict. The intent is to create a dual-purpose dwelling that encompasses both security and comfort, addressing the urgent needs of individuals in unstable environments. This design not only considers immediate safety but also aims to enhance the living experience within a context of adversity.
## Spatial Strategy and Materiality
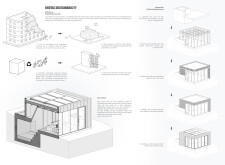
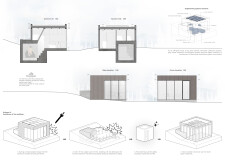
The architectural design prioritizes both resilience and livability through a well-considered spatial layout. It features a floor plan that includes essential living spaces—a kitchen, bathroom, and a multifunctional bedroom that doubles as a shelter. Expansive glass panels are incorporated to promote natural light and maintain a visual connection to the surrounding landscape, contributing to a tranquil atmosphere.
In terms of materiality, the Bunker House utilizes a combination of reinforced concrete for structural integrity and light wood, which contributes to a contemporary aesthetic while facilitating comfort. The design incorporates recycled materials from destroyed buildings, aligning with sustainability objectives. Solar panels are integrated to enhance energy efficiency, further reinforcing the commitment to environmentally responsible practices.
## Resilience and Adaptability
The Bunker House design emphasizes resilience in multiple dimensions. The lower section, constructed to withstand potential threats, serves as a protective haven. The modular nature of the building allows for continued safety even if the upper structure is compromised. Importantly, this design not only provides immediate refuge but also encourages community connectivity, as it is intended for use in conflict-affected areas, promoting a sense of solidarity among occupants.
Overall, the Bunker House exemplifies an innovative architectural solution capable of addressing both current humanitarian needs and future living conditions through its adaptive design and sustainable methodologies.