5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
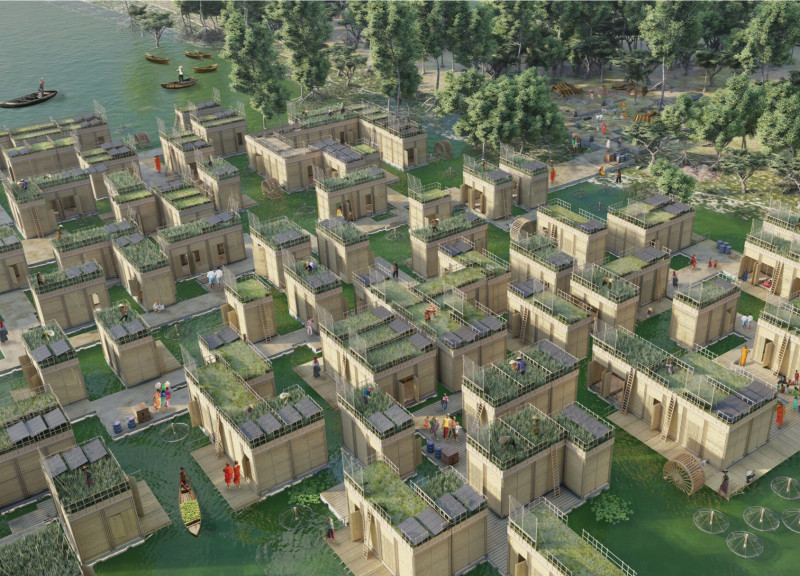
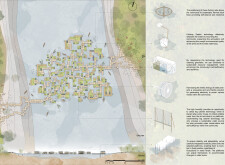
The Self-Sustaining Floating Adaptable Community (S.F.A.C.) is situated in Bangladesh, a region increasingly affected by rising water levels and climate change. The intent of the project is to establish a self-sufficient community that can adapt to environmental shifts while fostering social interactions among its residents. Through this design, the project aims to address both immediate housing needs and long-term ecological challenges.
### Spatial Efficiency and User-Centric Design
A modular design strategy is employed, with individual dwelling units measuring 2m x 3m. This configuration allows for flexible spatial arrangements, effectively accommodating various living functions such as cooking, storage, and sleeping. Each unit includes rooftop gardens, which facilitate local food production and community engagement. Shared communal areas are integrated into the design to promote collaboration and social cohesion, ensuring that essential services like education and healthcare are accessible to all residents.
### Sustainable Materiality and Resource Management
The selection of materials prioritizes local resources and sustainability. Structural components are primarily constructed from locally sourced wood and bamboo for their durability and ecological benefits. Reused water barrels serve as buoyancy elements in the floating platforms, while biobased insulation enhances thermal performance. An effective water management system incorporates rainwater harvesting and greywater treatment technologies, such as Seabin systems, to minimize environmental impact. In addition, the integration of photovoltaic panels ensures energy independence, harnessing renewable sources to meet community needs.
The design also emphasizes ecological integration, promoting biodiversity through initiatives like fish farming, which supports local food systems. This multi-faceted approach enables the community to withstand demographic fluctuations and environmental challenges over time.