5 key facts about this project
## Overview
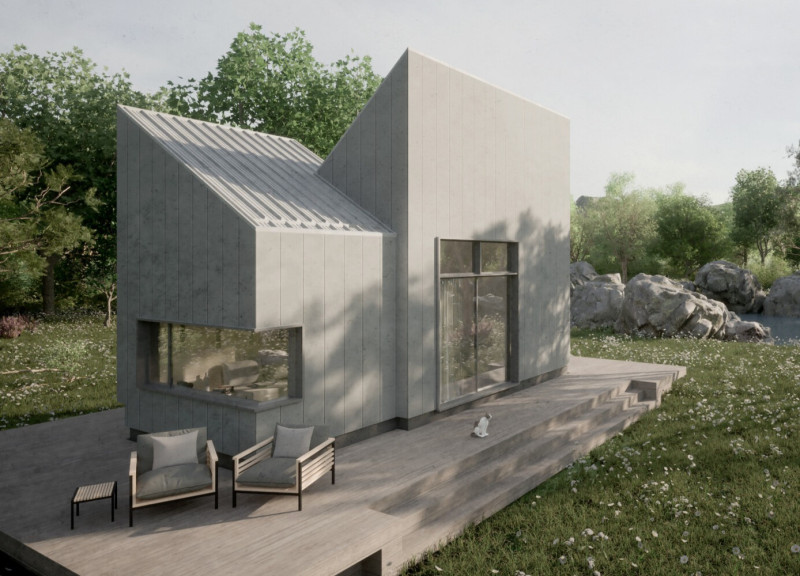
The Urqucito project, designed to address contemporary challenges related to climate change, is an off-grid microhome located in flood-prone areas. Its focus on innovative water management and sustainability reflects a growing need for efficient housing solutions in environments affected by rising water levels and increased flooding. The architectural framework emphasizes an adaptive relationship with water, positioning it as both a challenge and a resource.
### Spatial Strategy and Structural Design
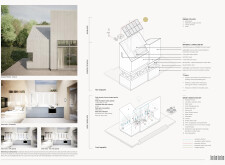
The structure features an angular silhouette characterized by slanted roofs and vertical planes, optimizing both water runoff during flooding and providing expansive views of the surrounding landscape. The design incorporates an "amphibious" strategy, allowing the dwelling to float during high water events while maintaining its structural integrity. This transitional interaction between the building and natural elements promotes a dynamic engagement with the environment.
### Material Selection and Sustainability
Incorporating a range of innovative materials, Urqucito emphasizes durability and sustainability. The roof and cladding utilize recycled aluminum for lightweight strength; an expanded polyethylene flotation system ensures buoyancy during severe weather; and high-performance concrete forms a resilient foundation to withstand floods. Sustainable insulation materials enhance energy efficiency, while low-emissivity glass windows contribute to thermal comfort, minimizing energy consumption.
### Water Management Systems
Urqucito integrates advanced water management features, including a comprehensive rainwater harvesting system that underscores water conservation efforts. The unique architectural design enables controlled water levels within a chamber during floods, enhancing safety while maintaining the dwelling's functionality. Additionally, an indoor water management system employs transparent tubing with colored LED indicators to promote awareness of water usage, encouraging responsible practices among residents. Equipped with solar panels and water recycling technologies, the microhome is capable of off-grid living, reinforcing its sustainability and resilience in various geographic contexts.