5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
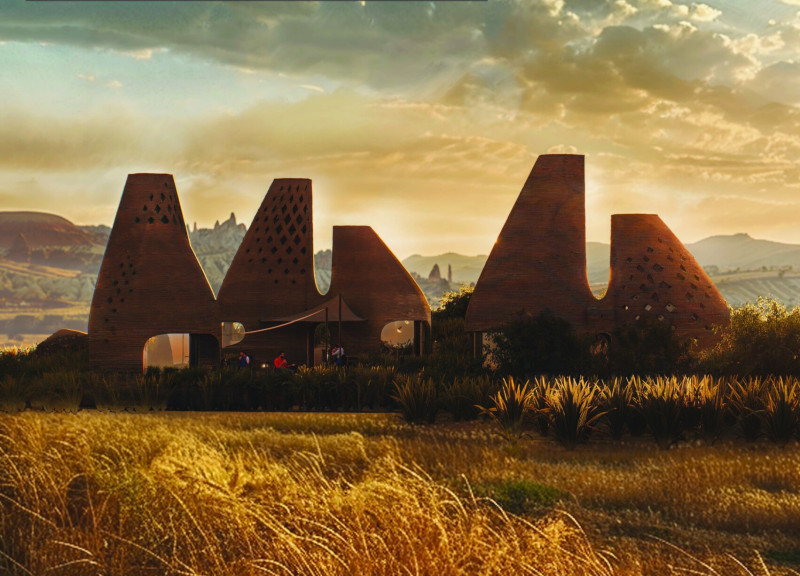
Cappadocia Retreats is an architectural initiative situated in Central Anatolia, Turkey, focusing on the sustainable reconstruction of dwellings in desert environments. The design integrates traditional architectural principles with modern technologies to address environmental and social needs in arid areas. Emphasizing energy efficiency and environmental adaptability, the project seeks visual harmony with the unique geological landscape of Cappadocia.
### Sustainable Material Practices
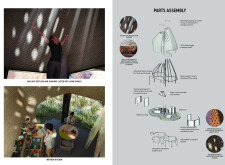
The project employs innovative methods for sourcing materials, utilizing excavated earth waste from existing construction sites for the 3D printing of building components. This approach minimizes environmental impact and promotes the use of sustainable materials. Key structural elements include concrete for durability, aluminum framing for thermal insulation, and specialized insulation materials such as rice husks. Additionally, the design incorporates glass sections to maximize daylight while maintaining indoor climate control.
### Spatial and Community Design
Architecturally, the structure features conical forms that resonate with the region's natural rock formations, facilitating airflow and creating varied light patterns throughout the day. Interior layouts promote communal living with open-plan kitchens and living spaces that encourage social interaction, while also providing private areas for residents. Communal gathering spaces are strategically integrated to foster social connectivity, enhancing the sense of community within the retreat.