5 key facts about this project
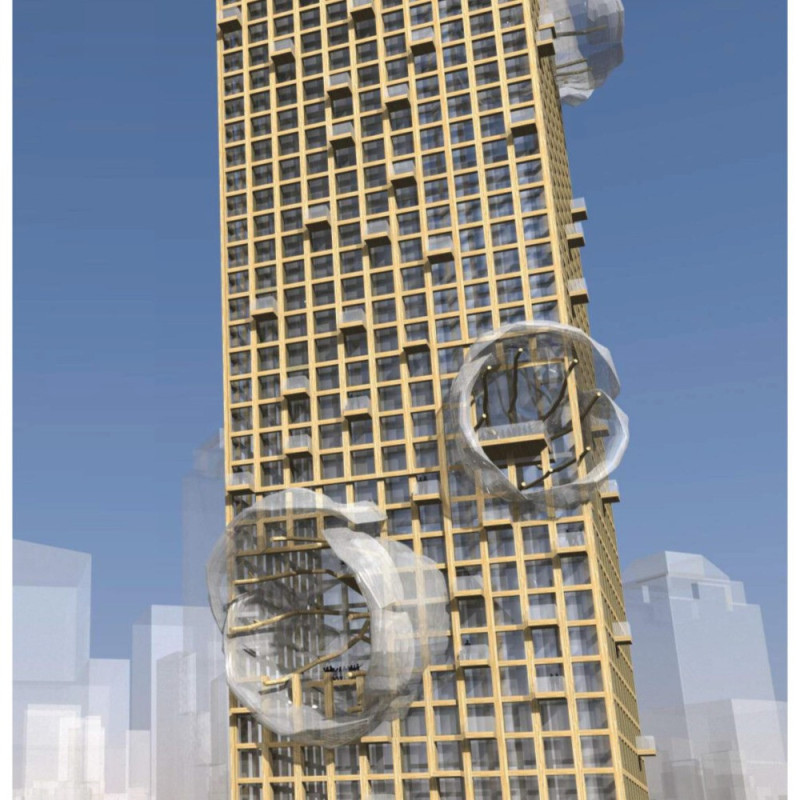
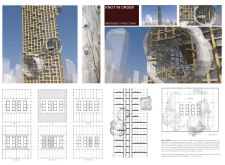
The Manhattan Timber Tower is a notable example of architectural design inspired by the Sequoia tree. Located in the bustling heart of Manhattan, it blends the need for functional spaces with lessons drawn from nature. The structure accommodates various uses, including offices, restrooms, a food court, a health club, a business center, and a small auditorium. The design concept highlights the balance between individuality and community, mirroring the unique traits of trees within a larger forest ecosystem.
Architectural Concept
The architectural idea focuses on the relationship between order and disorder, embodied by the knots and burls in the timber structure. Each timber member represents a unique genetic code, reflecting the diversity found in nature. These natural forms do more than add beauty. They create distinct spaces within the building that promote a sense of community and identity, similar to how neighborhoods develop in a forest.
Spatial Organization
The layout of the Manhattan Timber Tower is designed to enhance interaction among its various functional areas. Each space—offices, restrooms, food courts, and recreational facilities—has a specific role but connects easily with others. This thoughtful arrangement encourages movement and social engagement throughout the building, adapting to the busy pace of city life.
Materiality
Timber is the primary material used, illustrating a focus on sustainability and ecological awareness. This choice not only adds visual warmth to the structure but also strengthens the link between the building and its natural surroundings. The use of timber contrasts with typical materials found in urban settings, creating a more inviting environment for occupants and visitors.
The design pays careful attention to integrating natural characteristics, with pockets within the structure that reflect the intricate patterns found in trees. These features enhance the user experience and embody the principles of biomimicry and ecological balance, creating a harmonious relationship between the built environment and nature.