5 key facts about this project
### HIRABI Architectural Overview
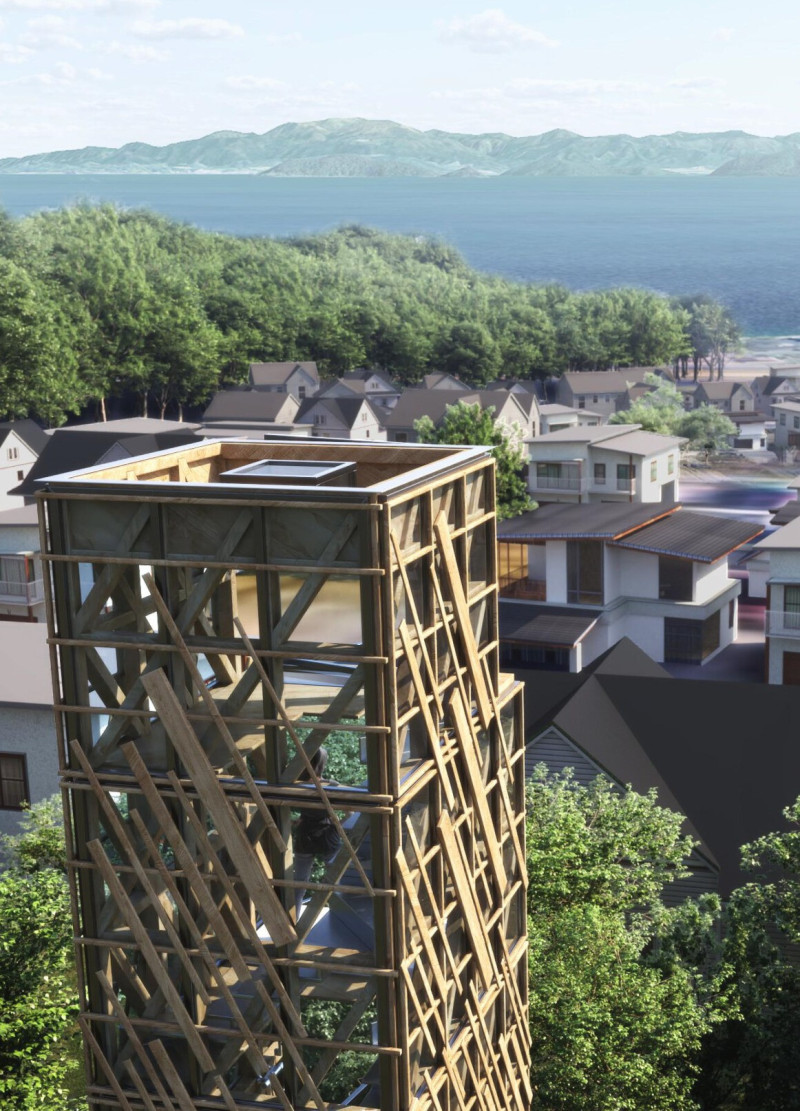
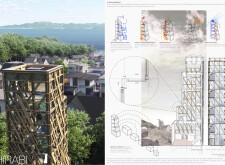
Located in Shiga Otsu, Japan, adjacent to Lake Biwa and at the base of the Hira Mountains, HIRABI is designed to foster a connection between its occupants and the surrounding landscape. The project serves as a multifunctional residential and studio space, contributing to both living and artistic expression. Its conceptual framework prioritizes flexibility and sustainability, responding to contemporary ecological concerns while promoting creative endeavors through its spatial organization and design.
#### Architectural Form and Spatial Strategy
The building's vertical profile is characterized by a lattice framework, constructed primarily of reclaimed timber and structural aluminum. Large windows and open spaces throughout the design facilitate natural light penetration and frame panoramic views of the Hira Mountains and Lake Biwa. This emphasis on openness encourages interaction with nature, enhancing the overall user experience. The building spans multiple levels, from two to five, with a layered arrangement that supports airflow and natural cooling, reinforcing energy-efficient living. Internal layouts prioritize accessibility and movement, with a central spiraling staircase connecting various levels and serving as a focal point for circulation.
#### Materiality and Sustainability
HIRABI employs a range of sustainable materials, including reclaimed timber sourced from decommissioned buildings, structural aluminum, double-glazed glass, and non-toxic finishes. The use of these materials not only underlines the project's commitment to environmental responsibility but also contributes to the building's aesthetic, providing warmth and texture. Advanced ecological systems, such as rainwater harvesting, photovoltaic solar panels, and wind harvesting technologies, enhance the building's self-sufficiency. Moreover, geothermal heating and cooling leverage the local climate, utilizing natural resources to minimize reliance on nonrenewable energy sources while effectively addressing the environmental impact of the design.