5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
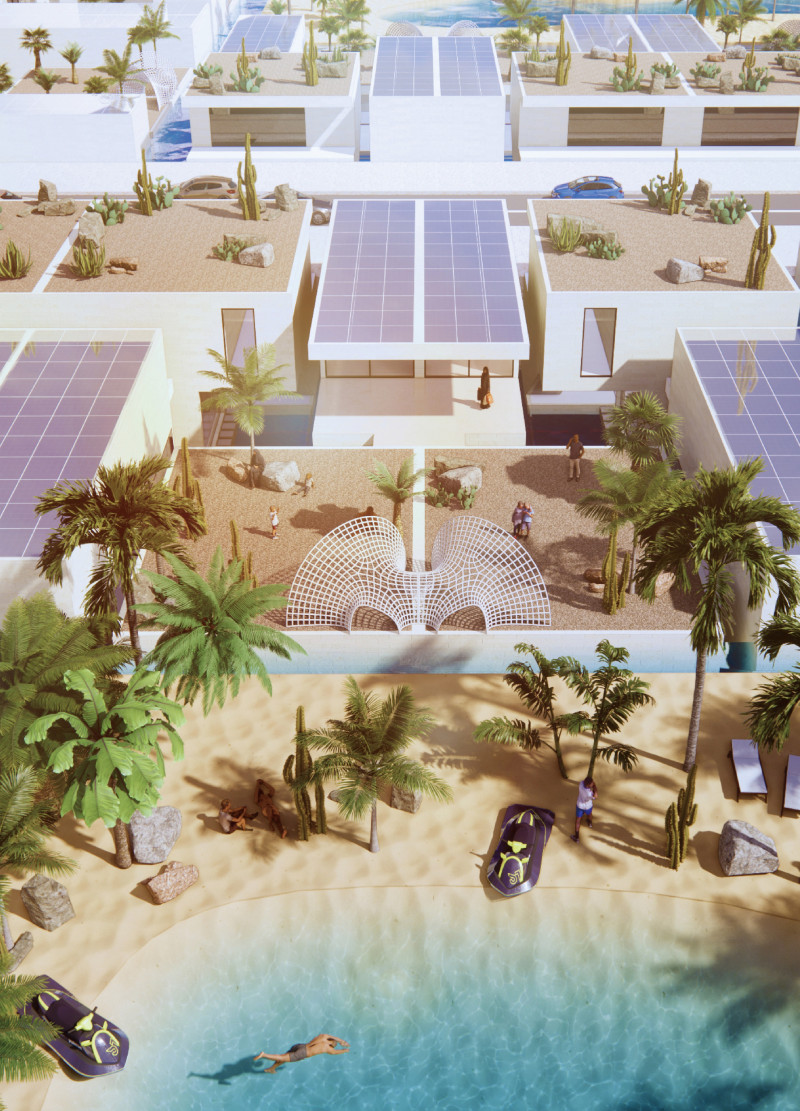
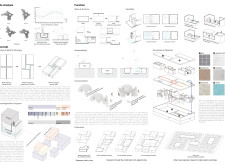
Oasis Housing is situated in a desert region, specifically designed to address the unique challenges posed by the climate while fostering a sense of community. The architectural intent emphasizes sustainable practices and natural integration, particularly the thoughtful use of water, to create comfortable living environments for residents. The design responds to the region's arid conditions while promoting social interaction and enhancing landscape connectivity.
### Spatial Organization and Community Engagement
The design capitalizes on the essential elements of water and wind, creating an architectural layout that enhances the living experience. Water features are incorporated not only for aesthetic appeal but also to provide functional cooling benefits. Structures are strategically oriented to optimize natural ventilation, thereby reducing reliance on mechanical systems. Communal spaces such as gardens and plazas are intentionally included to encourage social interactions among residents, supporting a cohesive community atmosphere.
### Material Selection and Sustainability
The project employs a range of innovative materials that contribute to both its functionality and aesthetics. Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) on rooftops enhance renewable energy use, while laminated concrete offers structural robustness and a modern aesthetic. Natural materials such as limestone and aggregate are utilized for their durability and ecological fit within the landscape. The incorporation of water through various features not only enhances the microclimate but also integrates seamlessly into the overall design, promoting an environmentally conscious living space that reflects a commitment to sustainability.