5 key facts about this project
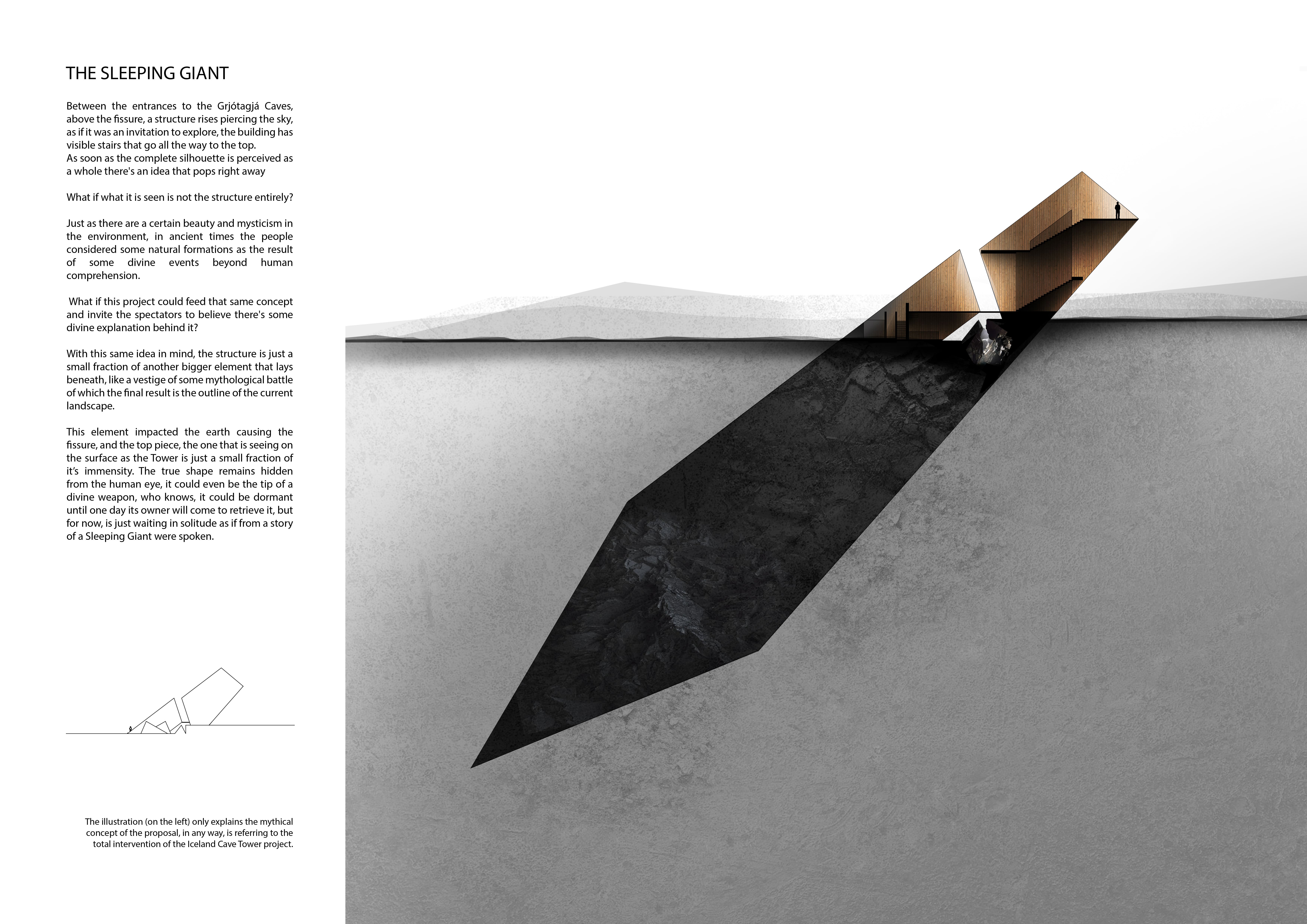
The project represents a blend of cultural significance and environmental integration. Designed with an emphasis on sustainability, it reflects a deep awareness of the local ecosystem while fostering a connection between mythology and contemporary architectural practices. This duality informs the approach to both the structure and the landscape.
Unique Design Elements
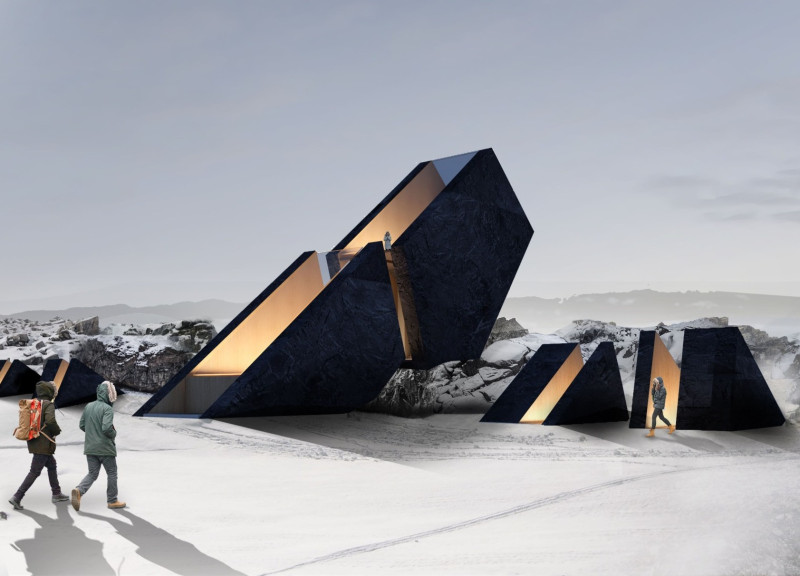
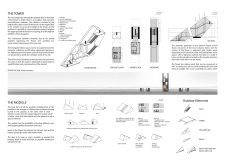
The design features angular, shard-like structures, echoing the existing geological formations in the area. This creates a harmonious dialogue between the architecture and the rugged terrain, which is characteristic of Iceland’s landscapes. The layout includes interconnected modules that serve diverse functions such as visitor information centers, rest areas, and restrooms. This modularity allows flexible use of space tailored to the varying needs of visitors.
The use of materials is particularly noteworthy, with volcanic stone sourced locally for the exterior. This choice not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also ensures a seamless transition between the tower and its environment. Inside, timber wood is utilized to add warmth, providing a comfortable contrast to the rough exterior. The design incorporates translucent roofing to maximize natural light and collect rainwater, contributing to its sustainability.
Strategically, the design promotes accessibility through well-defined pathways, guiding visitors toward key viewpoints and enabling exploration of the caves. The project encourages an immersive experience, allowing individuals to engage with both the building and the captivating landscape surrounding the Grjótagjá Caves.
Functional and Aesthetic Considerations
The architectural design marries function and aesthetics by enhancing the natural beauty of the site while providing necessary services for visitors. The varying heights of the structures create multiple vantage points for observing the landscape, reinforcing the project’s intent to foster a deeper connection between visitors and the environment. Moreover, the incorporation of sustainable practices—such as rainwater harvesting and small wind turbines—illustrates a commitment to eco-friendly architecture.
For a comprehensive understanding of The Sleeping Giant, interested readers are encouraged to explore the architectural plans, sections, and designs available through the project presentation. These elements provide further insights into the innovative design approaches that define this unique architectural endeavor.