5 key facts about this project
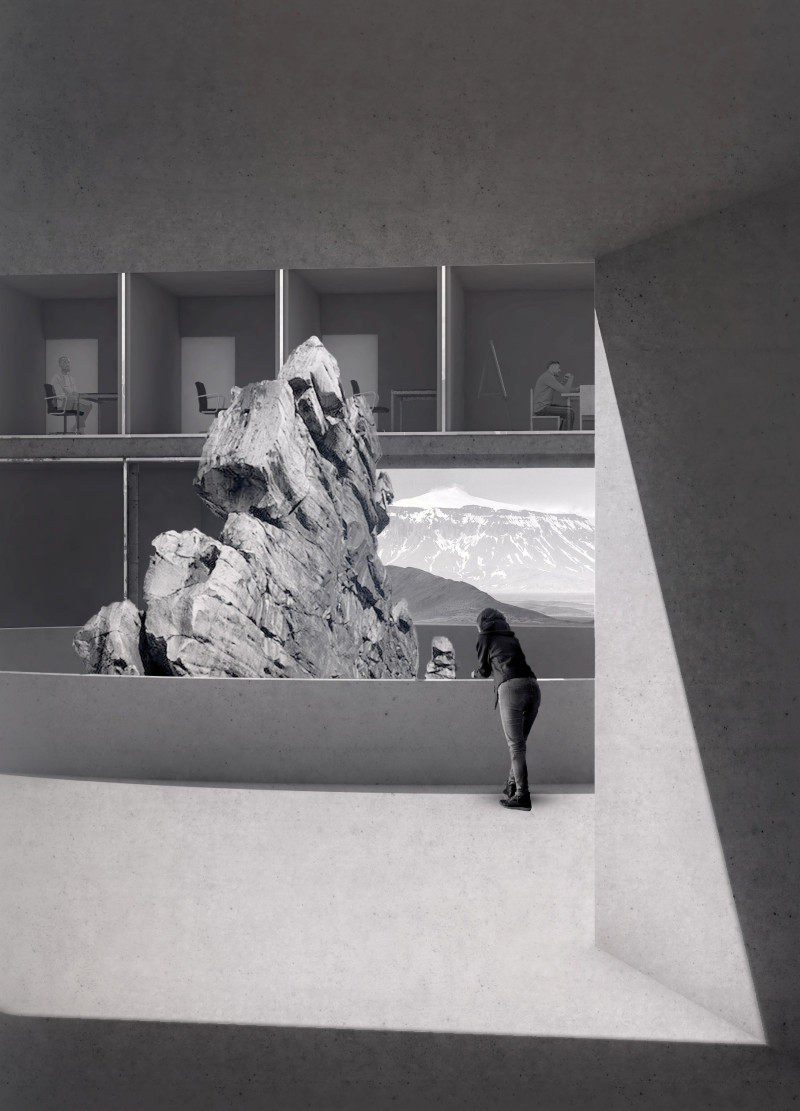
The Iceland Volcano Museum is an architectural project designed to showcase and educate visitors about the unique volcanic landscape of Iceland. Situated in a region characterized by its dramatic geological features, the museum serves as an informative center while reflecting the essence of Icelandic culture and its relationship with nature. The design is inspired by volcanic forms, merging functionality with aesthetic resonance, and creating a space that is both engaging and educational.
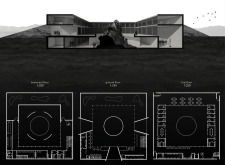
The museum incorporates exhibition spaces, a public café, and administrative offices, all organized to facilitate visitor movement and enhance the learning experience. The strategic layout accommodates the flow of visitors, creating an inviting atmosphere while maintaining the integrity of the exhibits. The architecture emphasizes a strong connection with the surrounding landscape, effectively drawing visitors into the natural environment that the museum aims to represent.
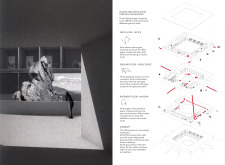
Unique Design Approaches One distinguishing feature of the museum's design is its integration with the landscape. The building's form mirrors the contours of volcanic formations, providing a visual representation of its purpose. The use of materials further emphasizes this connection; reinforced concrete evokes the strength of volcanic rock, while gravel and insulation materials specifically reference the natural terrain. Large glazing elements enhance the interior's relationship with the outside, framing views and allowing natural light to permeate the space.
Sustainability is a central theme throughout the project. The design incorporates earth-covered exterior walls, which not only minimize energy loss but also reflect traditional Icelandic architectural practices. This approach connects the building to its history and geography, instilling a sense of place within the modern architectural context. The careful selection of materials ensures durability against the region's challenging weather, while promoting energy efficiency.
Architectural Details The structural components of the museum are meticulously designed for both aesthetics and performance. The precast sandwich facade contributes to the building's thermal efficiency while offering a rugged texture that complements the surrounding landscape. Roof structures designed with lightweight gravel and robust drainage systems address environmental challenges, ensuring functionality without compromising the design ethos.
Interior spaces are planned to foster interaction and learning. The inclusion of an inner courtyard encourages communal gatherings and serves as a transitional space between exhibits. The use of acoustic panels enhances visitor comfort and engagement, creating a conducive environment for educational activities.
To explore this architectural project further, interested readers are encouraged to review the architectural plans, architectural sections, and architectural designs to gain deeper insights into the unique ideas and structural details of the Iceland Volcano Museum. The integration of modern design principles with ecological awareness presents an exemplary case of architecture that respects its environment while fulfilling its educational mission.