5 key facts about this project
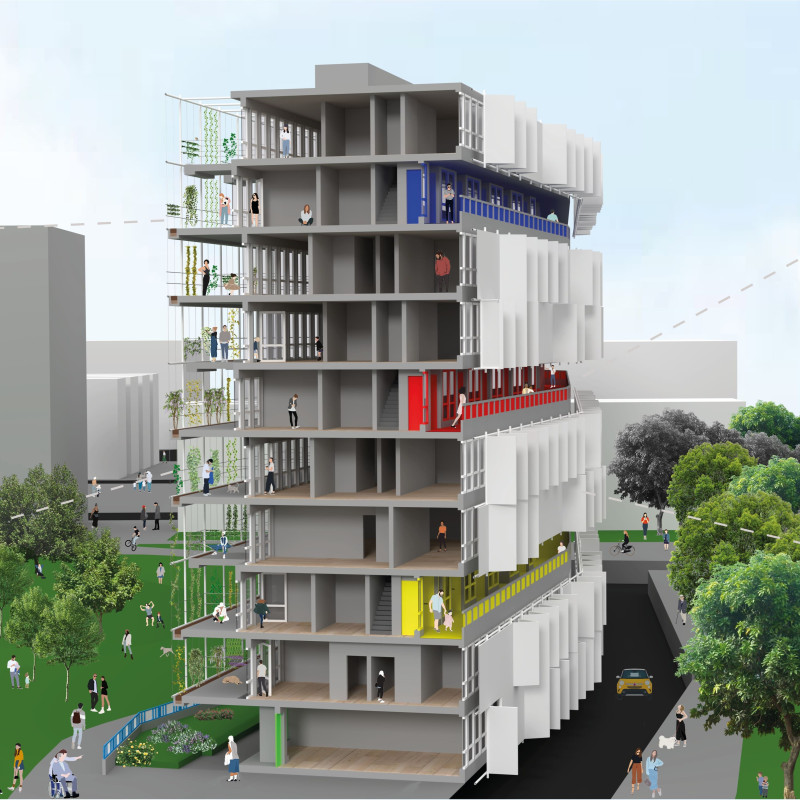
At its core, the project aims to create a vibrant living environment that caters to various demographics, particularly families and individuals seeking shared spaces that foster interaction. The design includes innovative housing models that offer flexible layouts, ensuring adaptability to the evolving needs of residents. This is achieved through the incorporation of modular components that can be configured in multiple ways to accommodate different family sizes and lifestyle preferences. The architectural design emphasizes communal living, with shared facilities such as laundry rooms, play areas, and communal gardens that promote social engagement among residents.
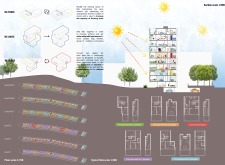
One of the key features of the design is the façade, characterized by a white grid structure that is not only visually appealing but also functional. This façade includes folding panels that provide adjustable shading and environmental protection, enabling the building to adapt to changing weather conditions. The integration of vertical gardens into the façade serves multiple purposes, enhancing the aesthetic quality of the building while contributing to its ecological footprint. These gardens play a critical role in improving air quality and supporting local biodiversity, further illustrating the project’s commitment to sustainability.
The materials used in the project reflect a balance of durability and aesthetic consideration. Concrete serves as the primary structural element, providing the necessary support for modular configurations and ensuring longevity. Glass elements within the vertical gardens optimize natural light while creating an inviting atmosphere in the communal areas. Additionally, PVC-coated steel utilized in the folding panels offers resilience against the elements, reinforcing the building’s adaptability. Wood features prominently in shared spaces, adding warmth and a sense of connection to nature, which can be essential in urban settings.
The landscape surrounding the building is designed to integrate seamlessly with the residential structures. Continuous green spaces link the inner environment of the project to external parks, providing residents easy access to nature and outdoor recreation. Elevated walkways, referred to as "streets in the air," enhance pedestrian connectivity while prioritizing safety and ease of movement. This design approach not only promotes interaction among community members but also encourages outdoor engagement, fostering a vibrant community life.
What sets this project apart is its emphasis on sustainability and community-oriented design principles. By focusing on modularity, the architectural design enables flexibility in living arrangements, reducing the overall environmental impact through efficient use of resources. The thoughtful integration of green spaces and community amenities creates an atmosphere conducive to social interaction, addressing the needs of a diverse urban population.
In summary, the "Sandwich" project in Blackwall offers a comprehensive architectural solution that prioritizes sustainability, functionality, and community cohesion. This project stands as a model for future developments, encouraging architects and urban planners to explore similar strategies in their design endeavors. To gain deeper insights into the architectural plans, sections, and design ideas of this project, it is encouraged for readers to explore the presentation of the project further.