5 key facts about this project
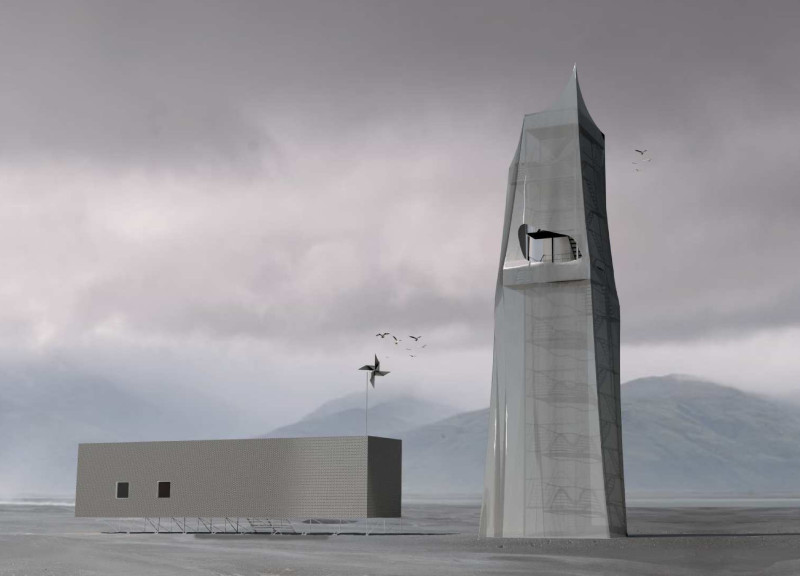
At its core, the Grjótágj Observation Tower represents a harmonious blend of cultural and geological significance, anchoring it firmly within the context of its location. It is strategically positioned to present visitors with opportunities to engage with the stunning Icelandic landscape while simultaneously highlighting the tectonic processes that shape the environment. This duality adds layers of meaning to the project, as it encourages a deeper appreciation for both the architecture and the natural features it seeks to complement.
The main function of the tower is to act as a viewing platform that offers panoramic vistas of the surrounding area. Visitors ascend the structure via a spiral staircase that facilitates an engaging journey upward, transforming the experience into an exploration of both space and landscape. The strategic placement of various openings within the tower allows for glimpses of the dramatic scenery, making the ascent an integral part of the overall user experience. In addition to its observational role, the tower houses essential visitor amenities, including a café, restrooms, and educational displays, enhancing its function as a comprehensive visitor center.
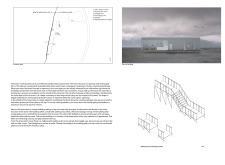
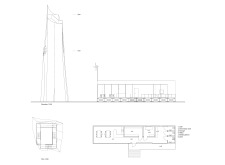
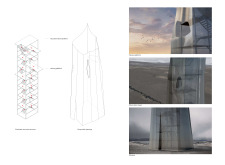
The design details of the Grjótágj Observation Tower are particularly noteworthy. The structure rises to a notable height of 22 meters, creating a vertical focal point that invites exploration. Its exterior features a drape concept, constructed from steel sheets that lend the tower a sense of lightness while ensuring durability against the harsh climatic conditions characteristic of Iceland. The draped quality of the outer layer allows for both transparency and reflection, with the façade catching light from the changing sky, thereby forging a connection with the surrounding environment. This design approach not only fulfills a functional requirement but also creates a visual dialogue between the building and the landscape, echoing the natural forms of nearby geological features.
The interior layout plays a vital role in how visitors interact with the tower and its surroundings. The inclusion of a spiral staircase is both functional and symbolic, guiding guests through a journey that culminates in a breathtaking view from the top platform. This thoughtfully designed staircase connects the various levels of the structure, allowing for visual continuity and an opportunity for visitors to pause and appreciate their surroundings as they rise. Additionally, the floor plan includes open spaces that mimic the organic formations of natural caves, creating an atmospheric experience that enhances the overall connection to nature.
Materiality is a key facet of the Grjótágj Observation Tower’s architectural integrity. The primary materials used in its construction include steel for the structure and extended steel sheets for the outer drape. These materials were selected not only for their structural advantages but also for their ability to withstand the local weather conditions. The glass windows integrated into the service building further enhance the design by allowing natural light to stream in and framing breathtaking views of the landscape. This careful consideration of materials underscores the project's commitment to sustainability and environmental respect.
The Grjótágj Observation Tower sets a benchmark for integrating architecture with natural and cultural narratives, providing a distinctive experience for visitors. Its unique design embraces a modern aesthetic while paying homage to the geological and historical significance of its location. The tower encourages exploration, engagement, and a deeper understanding of the interplay between humanity and nature.
Readers are invited to delve further into the project presentation to discover intricate architectural plans, sections, and designs that provide additional insights into the successful synthesis of form, function, and context within this architectural endeavor. The Grjótágj Observation Tower serves as an exemplary model for future architectural projects, emphasizing the importance of contextuality and environmental consciousness in modern design.