5 key facts about this project
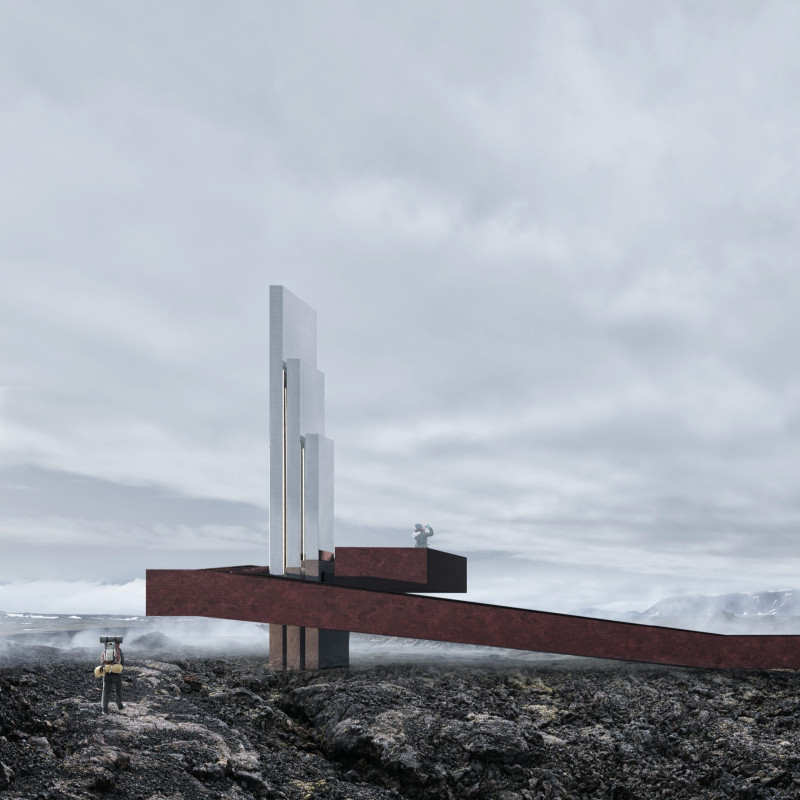
The Grotto functions primarily as a visitor center and shelter that allows explorers to retreat from the often harsh Icelandic weather. By employing local materials and sustainable practices, the architecture aims to minimize its environmental impact while enhancing the natural landscape's aesthetic.
Unique Architectural Features
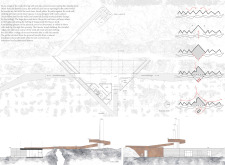
The design features angular forms that represent tectonic movement, resembling both an artificial cave and a natural formation. This concept showcases an intentional foray into integrating architecture with nature. A large glass roof allows natural light to filter into the space, simulating a fissure and providing a unique experience for visitors. The use of locally-sourced basalt for the facade not only strengthens the connection to the surrounding geology but also emphasizes the commitment to sustainability.
The pathway system is strategically designed to lead visitors through the site, encouraging exploration of both the architecture and the landscape. Personal viewing points and observation decks are incorporated to maximize engagement with the surrounding vistas, reinforcing the architectural experience as one that is deeply connected to its environment.
Material Considerations
The Grotto employs a range of materials consistent with its geographic context. Basalt plates form the external facade, paying homage to local geological features. Timber and weathered steel are used throughout the pathway and interior spaces for durability and to complement the rugged environment. Concrete pillars provide structural integrity while echoing the natural formations found within the area. Natural insulation materials have been integrated to enhance the building's thermal efficiency and overall sustainability.
The Grotto stands as a thoughtful piece of architecture that exemplifies the harmonious potential of built and natural environments. For a comprehensive review of the architectural plans, sections, designs, and ideas behind the project, exploring the full presentation will provide valuable insights into its broader implications in architectural practice.