5 key facts about this project
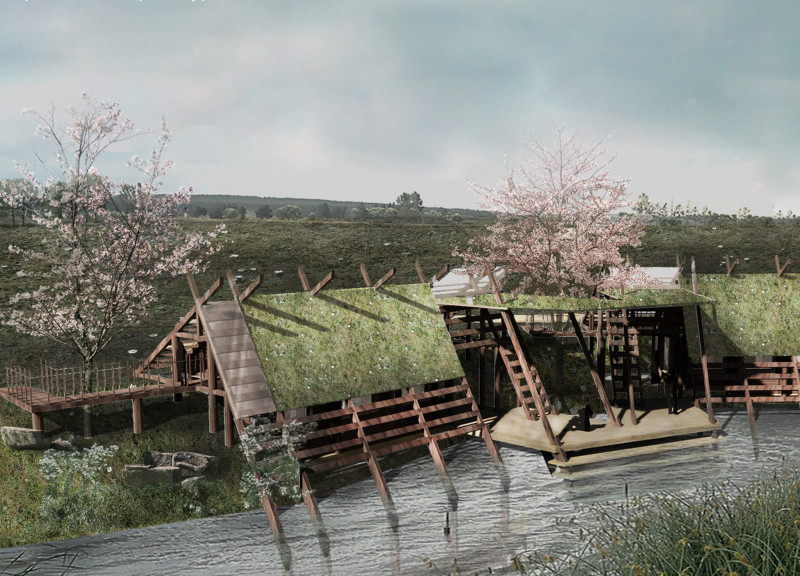
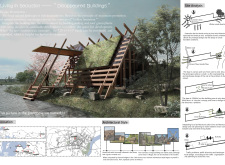
The project "Disappeared Buildings" is an innovative architectural design located in Skrunda, Latvia. It seeks to redefine the relationship between built structures and their natural surroundings by employing a concept of integration rather than opposition. The architecture utilizes sinking construction methods that allow the buildings to merge with the landscape and minimizes visual impact on the environment. The layout prioritizes ecological sustainability while facilitating functionality for community gatherings and tourism.
The project consists of modular designs that can adapt according to changing demands, reflecting an understanding of both current use cases and future growth potential. By employing green roofs and natural materials, the buildings promote biodiversity and support environmental longevity. This approach emphasizes the importance of maintaining a harmonious balance between human habitation and the preservation of natural resources.
Blending Traditional and Modern Techniques This project distinguishes itself through its use of traditional Latvian building methods, specifically regarding timber construction, while updating these techniques to align with contemporary environmental challenges. The integration of grass and plant life on the roofs enhances both aesthetic appeal and ecological value, promoting natural cooling and insulation. Such elements contribute to the project's overall sustainability and reduce energy consumption.
Architectural Elements and Organization Key components of the architectural design include sloped roofs that manage rainwater runoff and support plant growth. The spatial organization reflects a careful analysis of the site’s geographical features, ensuring that each building interacts appropriately with the terrain. Natural light is optimized through strategically placed windows, creating a connection between indoor and outdoor environments. The layout encourages social interaction among users while allowing for privacy when needed, showcasing a well-considered approach to community dynamics.
For detailed insights into the various aspects of the "Disappeared Buildings" project, including architectural plans, sections, and innovative design ideas, readers are encouraged to explore the project presentation further. This resource contains comprehensive information to enhance understanding of the architectural choices and environmental considerations that characterize this project.