5 key facts about this project
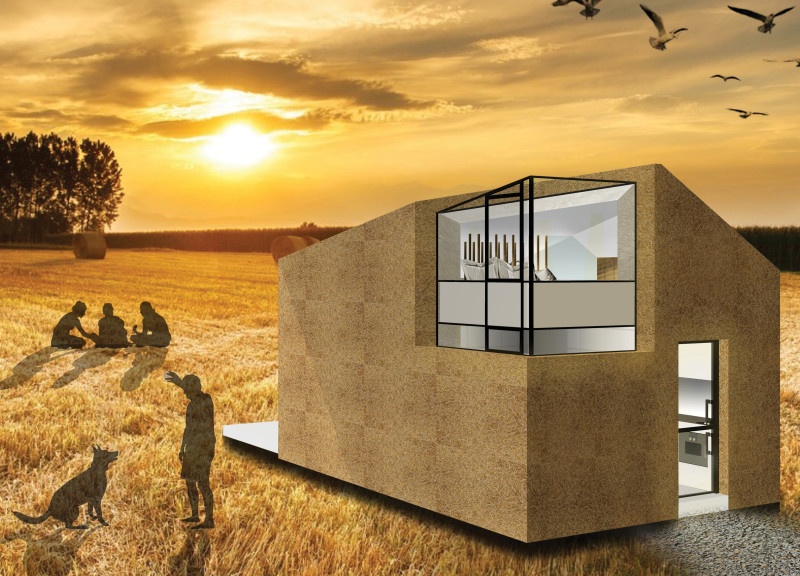
Sustainability is at the core of the design, employing materials that are not only eco-friendly but also promote renewable practices. The main construction materials include straw, reclaimed timber, recycled textile insulation, photovoltaic solar glass, and concrete. Each of these materials has been selected for their low environmental impact and efficiency in constructing energy-efficient living spaces.
One of the unique aspects of this project is its modularity. The microhome can be easily adapted to various user needs and environmental contexts, allowing for customization over time. This adaptability not only maximizes spatial efficiency but also enhances the lifespan of the structure. The design promotes multifunctional spaces where areas can serve multiple purposes, addressing the essential need for flexibility in modern living.
Natural ventilation is integrated into the design, optimizing airflow without relying on mechanical systems. This improves indoor air quality while reducing energy consumption. The inclusion of photovoltaic solar glass is another innovative feature, as it allows the facade to generate renewable energy while maintaining natural lighting within the home. This aspect aligns with modern architectural trends focusing on self-sufficiency and energy efficiency.
The emphasis on community integration further distinguishes the Smart Compostable and Reclaimed Microhome within the housing landscape. By encouraging shared resources and communal spaces, the project fosters social interactions among residents, promoting a sense of community.
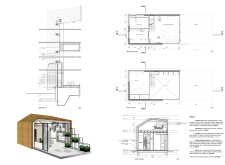
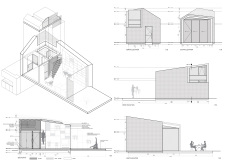
To gain deeper insights into this architectural endeavor, readers are encouraged to explore the presentation materials, including architectural plans, sections, and designs. These elements provide a comprehensive view of the methodologies employed and the thoughtful architectural ideas underlying this project.