5 key facts about this project
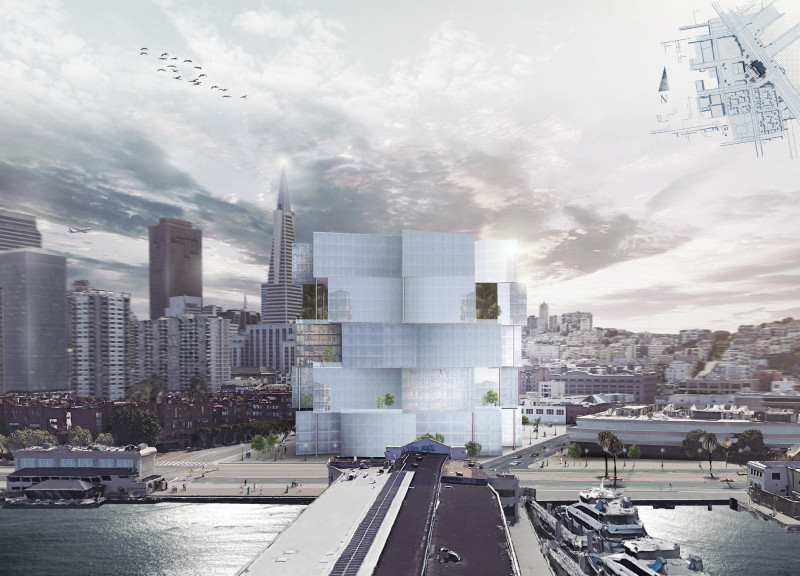
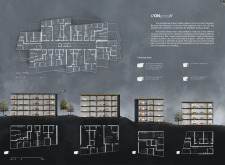
Functionally, the project serves as a multifaceted residential complex, accommodating a wide array of demographics including families, students, and professionals. This adaptability is central to the architectural design, as it allows for the stacking of living units in a manner that maximizes the vertical space of the site, thus creating an urban density that is both sensible and sustainable. By focusing on flexible layouts, the design supports various configurations ranging from single-person studios to larger family apartments. This diversity in housing types promotes inclusivity, addressing a critical need in the city where demographics are continually evolving.
The architectural layout features efficient spatial arrangements that prioritize functionality while also fostering a sense of connection among residents. The integration of communal spaces, such as lounges and rooftop gardens, encourages social interaction and community building, countering the isolating effects often experienced in high-density living environments. These shared areas are strategically placed to enhance accessibility, making it easy for residents to engage and collaborate in community activities.
One of the notable aspects of the project is its innovative use of materials, which reflects a commitment to sustainability and durability. The structure utilizes a metal frame as the backbone for its modular units, which provides a robust and secure foundation. Large glass panels make up much of the façade, allowing natural light to flood the interiors while fostering a connection between the indoor living spaces and the surrounding urban landscape. The use of insulation materials ensures that these spaces are energy-efficient, addressing both environmental concerns and the comfort of the residents.
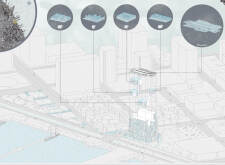
Another unique design approach is the factory-produced modularity, which allows the housing units to be assembled rapidly on-site. This method significantly reduces construction time and costs while lessening the environmental footprint typically associated with traditional building practices. By adopting this modular construction technique, the project not only meets urgent housing demands but also sets a precedent for future developments aimed at addressing urban housing challenges.
The architectural design also thoughtfully considers the natural environment. Rooftop gardens serve multiple purposes, offering green spaces that contribute to residents’ well-being and enhancing biodiversity. These areas are not just aesthetic additions; they also play a critical role in improving air quality and mitigating urban heat. By integrating nature into the design, the project underscores the importance of ecologically responsible architecture in urban settings.
Moreover, the project challenges conventional notions of affordable housing. Instead of being merely utilitarian, the design incorporates visual and spatial elements that enhance the quality of life for its inhabitants. The exterior treatment of the building celebrates contemporary aesthetics, combining functionality with modern design principles. This blend of style and utility reflects a growing trend in architecture that seeks to redefine what affordable living spaces can be, moving beyond the stigmas often associated with them.
For those interested in exploring the project's nuanced architectural designs, architectural plans, and sections in greater detail, further examination of these elements reveals a wealth of insights into the design process and outcomes. By delving into the specific architectural ideas demonstrated in this project, readers and stakeholders can better understand how innovative housing solutions can coexist with the urban fabric of cities like San Francisco. Engaging with this project's presentation offers an opportunity to appreciate the comprehensive thought and planning that define modern architecture in the context of contemporary urban living.