5 key facts about this project
Innovative Circulation and Spatial Configuration
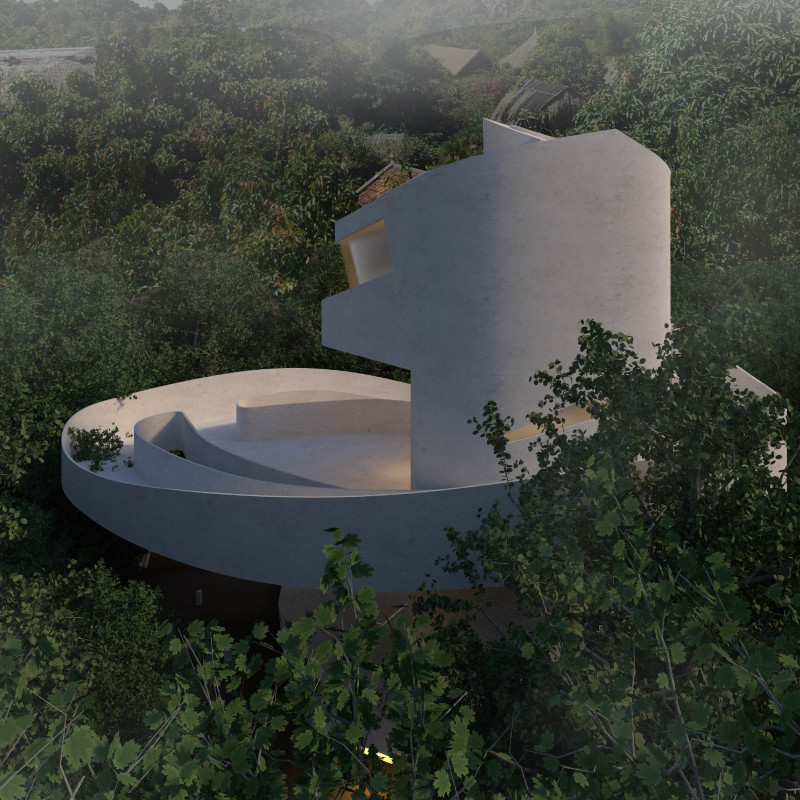
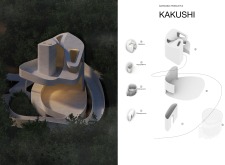
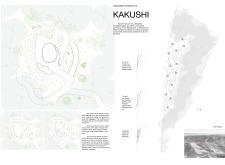
A notable aspect of the Kakushi project is the use of a spiral ramp system that facilitates movement between the various levels of the huts. This design choice not only enhances accessibility for all users but also generates a fluid transition between different spaces. Unlike traditional staircases, the ramp promotes a more dynamic interaction with the architecture, inviting visitors to explore and engage with the environment in a unique manner. The huts are positioned to form a network of pathways, encouraging social interaction and exploration, which distinguishes this project from many others that often prioritize isolated living units.
Sustainability and Material Utilization
The architecture of Kakushi employs a deliberate selection of materials, primarily concrete, glass, and wood, to align with its sustainable ethos. Concrete serves as the main structural element, providing durability, while glass allows for an abundance of natural light and views of the forest. Wood is utilized for interior finishes, contributing to a warm aesthetic that resonates with the natural landscape. The design prioritizes ecological sustainability, with a focus on preserving existing vegetation and optimizing natural light and ventilation. This thoughtful approach reduces energy consumption and enhances the overall sensitivity of the architecture toward its surroundings.
The Kakushi project exemplifies a refined architectural strategy that balances community, sustainability, and connection to nature. To explore the intricate architectural designs, sections, and plans that further illustrate these concepts, readers are encouraged to delve into the detailed project presentation.