5 key facts about this project
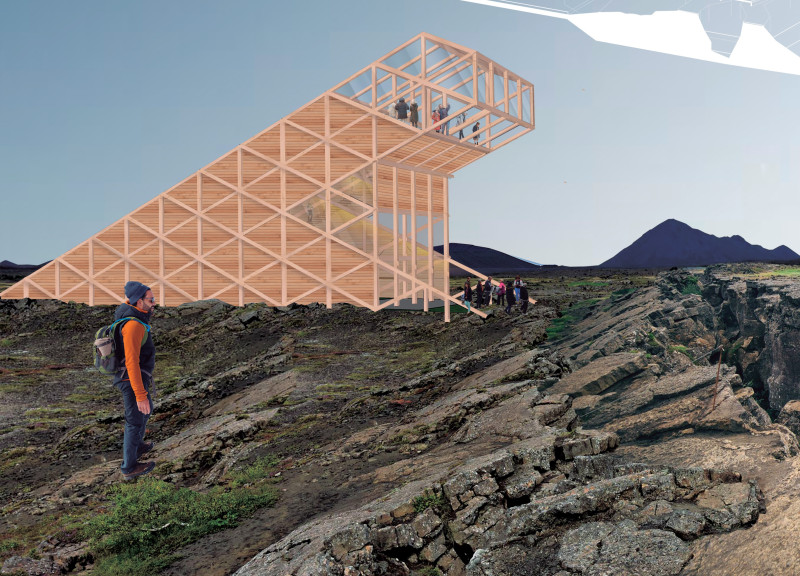
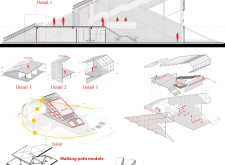
The tower consists of multiple levels, including observation platforms and functional spaces, such as bathrooms and utility areas. The design utilizes materials that reflect both the ecological concerns of the area and the aesthetic qualities of the landscape. Primary materials include laminated timber for structural elements, expansive glass for transparency and light, concrete for stability, and solar panels to promote energy efficiency.
Unique Materials and Design Approaches
One of the distinguishing features of Skadi Tower is its use of laminated timber, which emphasizes sustainability while providing structural integrity. This choice aligns with the project's ecological ethos, minimizing the environmental footprint during and after construction. The extensive use of glass allows for unobstructed views of the landscape, creating a seamless transition between the interior and exterior environments.
The design further innovates through its sloped form, which mimics the natural contours of the surrounding mountains. This approach not only aids in blending the construction with the site but also enhances the viewing experience as visitors ascend through the building. The layout guides visitors from intimate, enclosed spaces in the lower levels to more open and elevated observation areas, facilitating a diverse journey through the structure.
Functional Zones and Spatial Characteristics
The project includes clearly defined zones that cater to overlapping functions. Lower levels are dedicated to utility and access, ensuring that the essential services do not detract from the visitor experience. As one ascends, the design transitions into spaces dedicated to observation, offering panoramic views of the majestic Icelandic landscape.
Sustainable features integrated into the design include solar panels positioned to maximize sunlight conversion, thereby promoting energy efficiency. The building prioritizes natural lighting and ventilation, reducing reliance on artificial systems and enhancing the overall environmental performance.
Skadi Tower stands as a refined example of how contemporary architectural practices can address the nuances of natural landscapes while providing functional and aesthetically pleasing structures. It invites exploration not just through its physical spaces, but also through its architectural ideas, plans, and sections, offering a deeper understanding of its design principles and methodologies.
To learn more about the Skadi Tower project, including detailed architectural plans and unique design concepts, please explore the project presentation for an in-depth look at this innovative endeavor.