5 key facts about this project
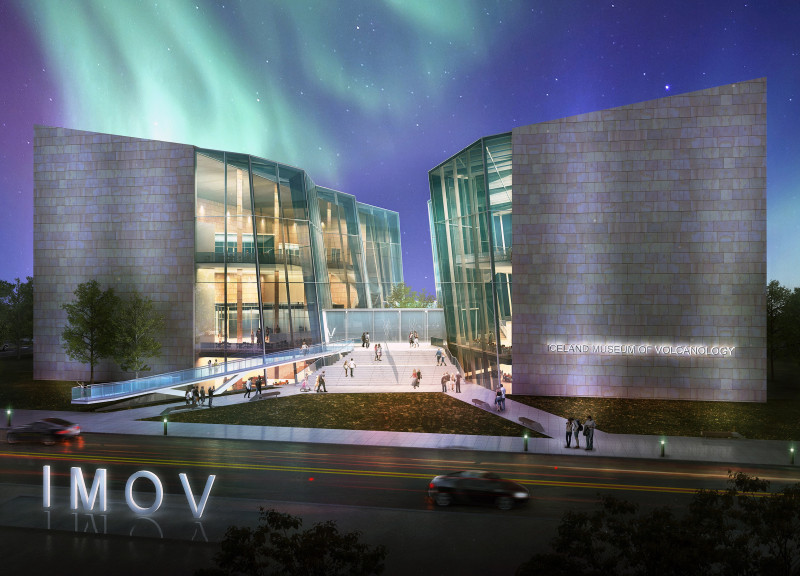
The primary purpose of the museum is to provide an engaging platform for learning about Iceland’s volcanic terrain. It incorporates exhibition spaces, a visitor center, conference facilities, and educational resources. Through its design, the museum not only displays artifacts and interactive exhibits but also delivers a narrative that connects visitors with the dynamic geology of Iceland.
Unique Design Approaches
One of the distinct features of the Iceland Museum of Volcanology is its use of local materials, including red rhyolite, which integrates the building into the surrounding environment. The design incorporates extensive glass facades, enhancing visibility and allowing natural light to permeate the interior. This transparent quality encourages a visual connection to the outdoor landscape, making the surrounding geological formations an integral part of the visitor experience.
The design also utilizes sloped roofing equipped with photovoltaic panels, signifying a commitment to sustainability. The incorporation of geothermal systems minimizes the building's energy footprint, aligning with Iceland's natural resources and environmental goals. The museum's layout, featuring interconnected buildings and green spaces, fosters interaction among visitors, enriching their understanding of volcanic processes.
Interior spaces are characterized by an expansive atrium that promotes movement and interaction, while flexible exhibition halls are adaptable for various displays. Visitors are invited to explore these thoughtfully designed areas, which enhance educational engagement while maintaining a sense of openness.
Visitor Experience and Engagement
The Iceland Museum of Volcanology emphasizes a holistic visitor experience through its architecture and design. Each section of the building is carefully crafted to support educational initiatives, including interactive displays and informative signage. The integration of outdoor landscapes, walkways, and seating areas creates a conducive environment for learning and leisure, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in the subject matter.
With clear connections between the building's architecture and the thematic content it presents, the project illustrates the interplay between built form and natural features. The architectural design embodies a balance between functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability, setting a precedent for future projects in the region.
For those looking to delve deeper into this architectural project, exploring the architectural plans, sections, designs, and ideas will offer a comprehensive understanding of the museum's conception, functionality, and significance within the broader context of Iceland's geological heritage.