5 key facts about this project
The museum incorporates various components and spaces, including exhibition halls, educational facilities, and social areas. These spaces are interconnected, allowing for a smooth flow of movement throughout the facility. Materials selected for the design include polished aluminum, light-colored wood, concrete, and ETFE cushions. Polished aluminum is used for its reflective nature, helping the structure blend with the surrounding environment, while wood adds warmth to the interior spaces. Concrete serves as the primary structural element, signifying stability. The use of ETFE cushions allows for natural light to permeate the building while contributing to energy efficiency.
Unique Design Approaches
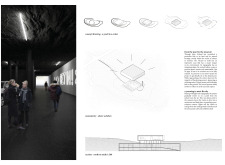
One of the standout features of the Iceland Volcano Museum is its emphasis on integrating the building with its natural surroundings. The architectural design mimics the volcanic landscape, with forms and shapes inspired by geological features. Large windows provide expansive views, effectively bringing the outdoors inside and maintaining a connection with the site. The manipulation of light is a critical aspect of the design, utilizing natural light to create varying atmospheres throughout the day. This approach enhances the visitor experience, fostering a sense of connection with the natural world and emphasizing the museum's focus on geology.
Considerable attention has been given to the interaction between indoor and outdoor spaces. Terraces and outdoor seating are strategically incorporated, further blurring the lines between the interior and the surrounding environment. This design aspect not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the museum but also promotes exploration and engagement with the landscape.
Innovative Sustainability Features
The architectural design of the museum incorporates sustainable practices while prioritizing energy efficiency. The ETFE cushions can be adjusted to control light and temperature, allowing for natural ventilation during warmer months and heat retention in winter. This adaptability contributes to the museum's overall environmental responsibility, aligning with contemporary architectural practices that emphasize sustainability. Additionally, the selection of durable materials, such as concrete and aluminum, reinforces the longevity of the structure.
For those interested in a comprehensive review of the Iceland Volcano Museum, exploring elements such as architectural plans, architectural sections, and architectural designs will provide a deeper understanding of the project's intricacies and innovative ideas. The architectural narrative of this museum underscores its significance as both a cultural and educational space dedicated to the understanding and appreciation of volcanic landscapes.