5 key facts about this project
### Overview
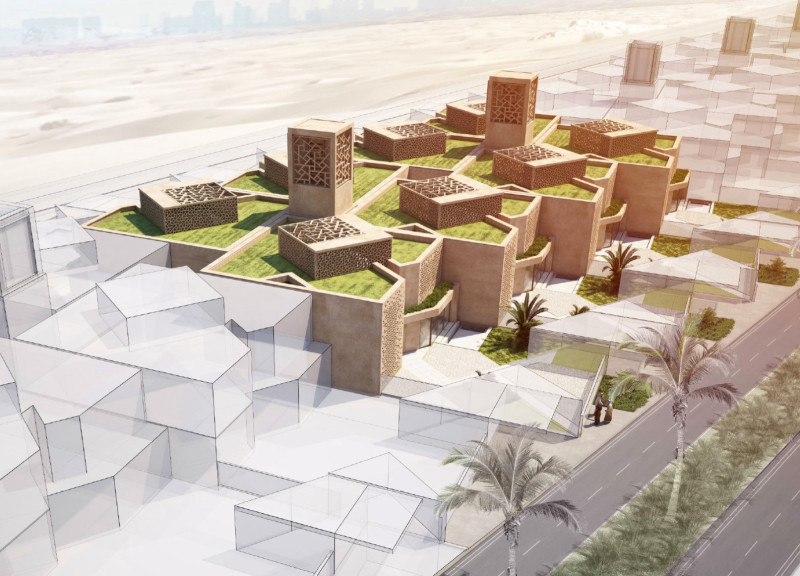
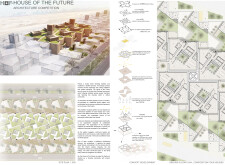
Located in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the House of the Future is designed to synthesize traditional Islamic architectural principles with contemporary design methodologies. The intent of the project is to foster a sustainable community that resonates with the cultural context of the UAE, encouraging unity and shared experiences among residents. This report examines the principal design elements, materials used, and innovative concepts integrated into the project.
### Community-Centric Design
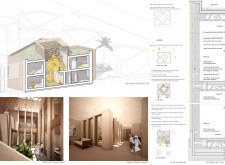
The layout of the House of the Future is organized to enhance community interaction, creating a microcosm of social relationships among residents. Each living unit is interconnected with shared spaces, promoting engagement while preserving individual privacy. This design strategy incorporates private courtyards that function as communal gathering areas, fostering a sense of belonging while serving the diverse needs of the inhabitants. Furthermore, the modular approach allows for scalability, enabling additional units to be added over time, thus adapting to changing community dynamics.
### Material Innovation and Sustainability
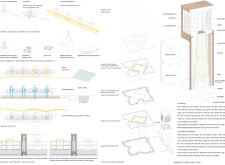
The design employs a range of materials that prioritize sustainability and modern construction techniques. Key components include rammed earth for walls, which enhances thermal mass and natural cooling, and lightweight concrete for structural flexibility. Extensive use of glass in windows maximizes natural light, improving indoor environmental quality. The incorporation of green roof systems contributes to thermal performance and biodiversity, while prefabricated elements streamline construction processes, minimizing waste. Additionally, a focus on natural ventilation through windcatchers and strategic unit orientation reduces dependence on mechanical cooling systems. The integration of solar panels and advanced water management systems, including rainwater harvesting, aligns the project with sustainable practices appropriate for the arid climate of Dubai.