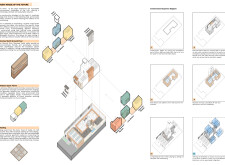
5 key facts about this project
### Overview
Located in Dubai, this residence is conceived to address the specific environmental challenges of the region. The design focuses on creating an energy-efficient habitat that reduces dependency on traditional cooling solutions while leveraging natural resources to promote sustainable living. The project employs a hybrid construction approach, integrating traditional craftsmanship with modern modular techniques to enhance thermal comfort and facilitate efficient assembly.
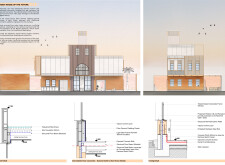
### Material Selection and Performance
The material selection is integral to the building's performance and aesthetic characteristics:
- **Rammed Earth**: Utilized for the ground floor walls, rammed earth provides significant thermal mass, effectively regulating interior temperatures and promoting energy efficiency by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night.
- **Fiber Cement Cladding**: Applied to the upper floors, these panels contrast with the rammed earth base and offer durability while balancing the overall visual composition of the structure.
- **Wood from Palm Trees**: This material adds a tactile element to the architecture, prominently featured in shaded canopies that reflect traditional Middle Eastern designs.
- **Glazing Solutions**: Triple-glazed windows are strategically installed to optimize natural light, reducing heat gain and enhancing interior comfort without the need for excessive artificial lighting.
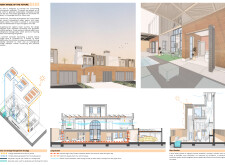
### Spatial Configuration and Adaptability
The villa's spatial organization across three levels fosters both functionality and flexibility:
- **Ground Floor**: The open-plan layout includes a living area designed for seamless interaction with an outdoor garden. Kitchen and dining spaces incorporate movable elements, allowing for adaptable configurations.
- **Upper Levels**: The first and second floors contain sleeping modules that can be added or removed based on evolving family needs, demonstrating an innovative approach to residential design that accommodates lifestyle changes.
### Environmental Integration
Sustainability is a core tenet of the project, manifested through various ecological features:
- **Solar and Wind Energy**: Roof-mounted solar panels and a wind tower contribute to energy generation and improve natural ventilation, reducing reliance on mechanical systems.
- **Water Resource Management**: The design incorporates rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling systems, efficiently storing water in a shared underground tank and promoting sustainable irrigation practices.
- **Natural Climate Control**: Cross-ventilation strategies, along with the building's thermal mass, facilitate effective temperature regulation, minimizing the need for artificial heating or cooling solutions.
This residence exemplifies how architecture can adapt to environmental constraints while offering a flexible and responsive living environment.