5 key facts about this project
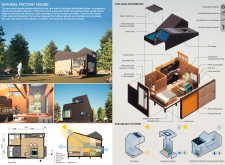
Designed to operate as a zero-carbon home, the Natural Factory House incorporates a variety of innovative features that promote a lifestyle aligned with nature. The primary function of this building is to provide a living environment that minimizes reliance on external resources, making it both a practical and environmentally-responsible choice for modern living. This is achieved through the integration of solar energy, water harvesting, and food production systems within the home itself.
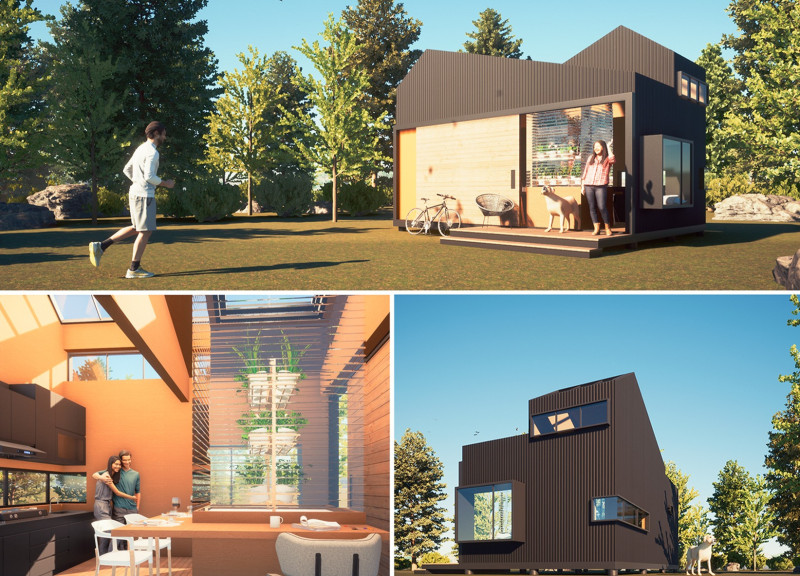
At the core of the project are several important elements that work together to create a self-sufficient household. The architecture utilizes a range of durable and sustainable materials, such as plywood with foam insulation, metal sheets with Galvalume coating, and transparent polycarbonate panels. These materials are not only functional but also contribute to the overall aesthetic, reflecting a modern yet warm atmosphere that encourages a strong connection to the surrounding environment. The use of wood in flooring and structural components provides a contrasting texture while enhancing the natural appeal of the interior spaces.
The design features of the Natural Factory House are particularly notable for their uniqueness. The open-plan layout fosters a fluid flow between living areas, encouraging interaction among occupants while simultaneously connecting indoor spaces with the outdoor landscape. Large glass sliding doors provide an unobstructed view of the exterior and facilitate natural ventilation, enhancing the indoor climate and reducing energy costs associated with heating and cooling.
Another significant design aspect is the incorporation of aquaponic systems, which allow occupants to engage in food production within their own home. This closed-loop system combines fish farming with plant cultivation, creating a sustainable source of food that further reduces the household's ecological footprint. Additionally, the house is equipped with water tanks that effectively collect and manage rainwater and greywater, emphasizing efficient water usage and conservation.
In terms of energy management, photovoltaic panels are strategically placed to maximize solar exposure, enabling the home to generate its own electricity. This feature aligns with the overarching goal of achieving a net-zero energy consumption rate, making the Natural Factory House an exemplary model of modern architecture that champions sustainability while meeting the practical needs of its residents.
The project stands out due to its adaptability to various geographical contexts, allowing for a flexible footprint that can be customized to different sites. This versatility is crucial in promoting the widespread adoption of sustainable living practices, as it enables potential homeowners to integrate eco-friendly designs into their unique environments.
Further exploration of this project provides an opportunity to delve deeper into the architectural plans, sections, and overall design ideas that have shaped the Natural Factory House. Understanding the architectural intricacies and design rationale is essential for grasping the full potential of this progressive living space. Readers are invited to further investigate the presentation of this project to uncover additional insights and details that highlight its innovative approach to sustainable architecture.