5 key facts about this project
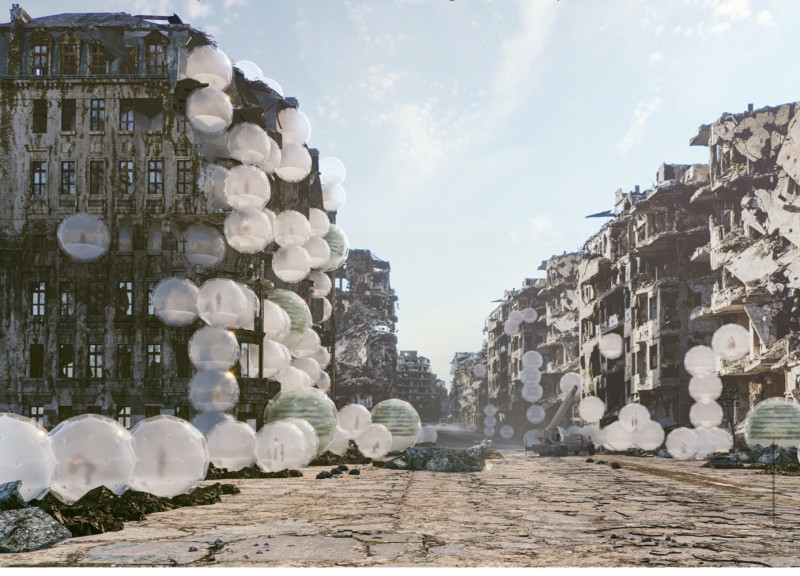
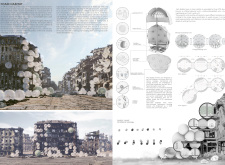
This architectural design embodies a unique approach to living in challenging environments. By leveraging inflatable architecture, the project showcases a contemporary interpretation of shelter that prioritizes ease of deployment and adaptability. The use of lightweight materials such as ETFE, a high-performance polymer, allows the structural elements to be both resilient and efficient. As a result, the Bubble Homes are constructed in a manner that facilitates quick assembly, enabling immediate occupation in times of crisis.
The functionality of the Foam Habitat is built into every aspect of its design. Each unit features three distinct spherical sections—kitchen/dining, living/sleeping, and mechanical/utility—creating a harmonious flow of interconnected spaces. This modular design not only optimizes the interior for various uses but also allows residents to customize their living experience according to their needs. The architectural plans reflect a careful consideration of communal and personal spaces, supporting interaction and togetherness while respecting individual privacy.
The architectural design integrates innovative systems that promote self-sufficiency. The incorporation of a hydroponic farming system within the community underscores the project’s commitment to sustainability. These farming units provide a local source of food, which is crucial in environments where resources may be scarce. Moreover, a closed-loop water recycling system ensures that water use is optimized and energy consumption minimized. The built-in fresh air fan and renewable energy lighting solutions further enhance the livability of the spaces, making them suitable for long-term habitation.
One notable aspect of the Foam Habitat project is its aesthetic quality. The organic, bubble-like forms of the units create a playful yet functional appearance that resonates with the surrounding urban landscape. By softening the harshness often found in city environments, the design not only attracts attention but also fosters a sense of refuge. The reflective qualities of the ETFE surfaces play a significant role, allowing these homes to blend seamlessly with their environment while creating a visually welcoming atmosphere.
The emphasis on community within the Foam Habitat is another fundamental element of the design. The layout encourages social engagement, with communal areas that prioritize interaction among residents. This strong focus on community building reflects a deeper understanding of human needs in crisis situations, where social bonds can provide vital support. The project highlights the importance of collaboration and shared experiences in constructing resilient societies.
What makes the Foam Habitat distinct is its ability to merge functionality, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal. By exploring innovative materials and efficient design strategies, this project positions itself as a model for future architectural endeavors that seek to address pressing global issues. The concepts presented in the Foam Habitat invite broader discussions around the integration of architecture into urban recovery efforts and the role of design in promoting ecological harmony and community resilience.
For those interested in exploring this project further, a detailed examination of the architectural plans, sections, and various design ideas will provide deeper insights into the innovative approaches employed in the Foam Habitat project. Understanding these elements can offer valuable lessons on how architecture can effectively respond to contemporary challenges, highlighting the crucial interplay between design and human experience in the built environment.