5 key facts about this project
### Overview
The Sunflower Project focuses on the adaptive reuse of shipping containers to create sustainable living environments. Designed to address environmental concerns and resource management, the project emphasizes ecological responsibility and functional design. Although the specific location remains unspecified, the adaptability of the design suggests applicability across various geographical contexts.
### Spatial Adaptability and Material Efficiency
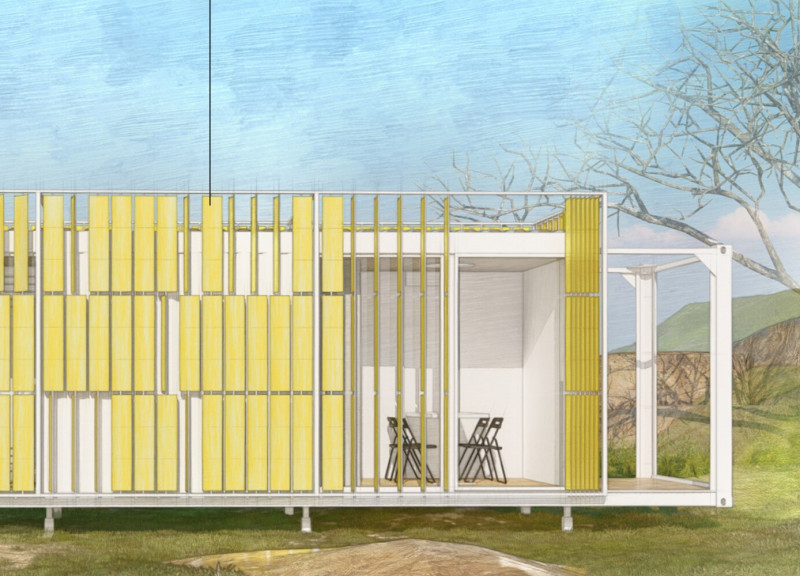
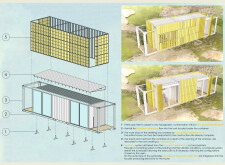
The primary design strategy involves transforming shipping containers into residential units, thereby minimizing the environmental impact associated with conventional construction methods. The use of **Container HC 40** ensures structural integrity and durability while allowing for efficient site preparation. Key features include telescopic feet that accommodate uneven terrain, facilitating rapid deployment in diverse settings, such as temporary housing or emergency shelters.
### Sustainable Systems and User-Centric Technologies
A crucial aspect of the project is the integration of renewable energy systems and water management solutions. Photovoltaic films incorporated into adjustable sunshades provide energy generation while optimizing natural light control. Rainwater capture systems are designed to enhance water sustainability. The interior employs **Troldtekt panels** for their acoustic properties and safe, eco-friendly composition, creating a comfortable living environment. Additionally, smart home technologies enable residents to monitor and control energy use effectively, tailoring the living space to individual preferences and environmental conditions.