5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
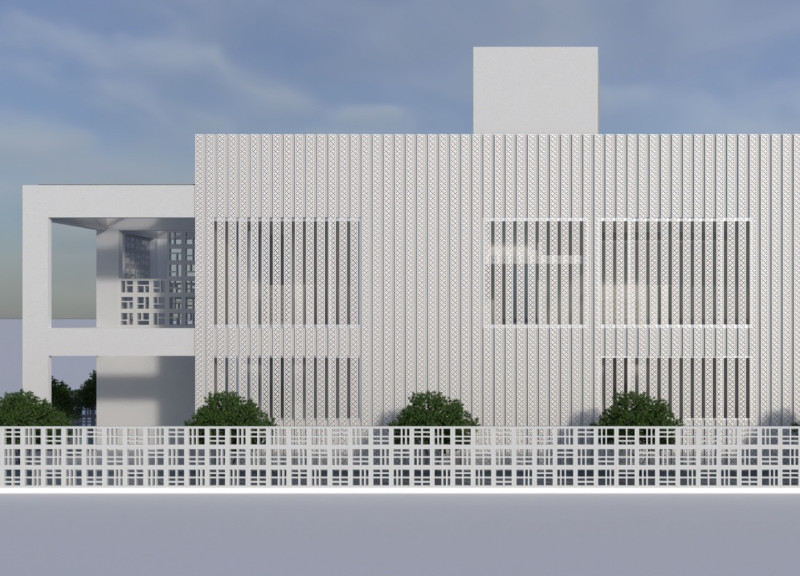
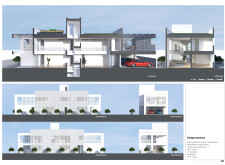
The Large Void House is situated in a culturally rich region that draws on Arabian design principles. The intent is to create a residence that fosters social interaction and environmental awareness through thoughtful architectural choices. Central to the design is a large void that promotes connectivity among family members while enhancing natural airflow and light penetration throughout the space.
### Spatial Configuration and Flexibility
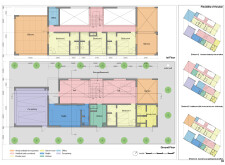
The residence is organized over two floors with an additional basement. The ground floor is characterized by several key areas designed for communal living, including a majlis for gatherings, a spacious kitchen that opens to living areas, and versatile rooms that can function as offices or guest accommodations. Privacy and accessibility are considered in the arrangement of the bedrooms.
On the first floor, additional bedrooms and a dedicated office space provide options for remote work. Balconies designed for leisure and interaction are incorporated, allowing for adaptability in use as the family's needs evolve. This flexibility is a core feature, reflecting contemporary living requirements and the potential for future reconfiguration.
### Material Selection and Sustainability
Careful attention has been paid to materiality, with reinforced concrete serving as the primary structural element for durability. Perforated grating not only adds a decorative aspect but also facilitates ventilation while offering a cultural aesthetic reminiscent of traditional Arabian designs. Generous glass openings enhance natural daylighting, reducing the need for artificial light.
Sustainability initiatives embedded in the design include cross-ventilation systems that utilize the void for natural cooling, photovoltaic panels that contribute to energy independence, and a green roof that enhances thermal insulation and supports urban gardening. These strategies reflect a commitment to maintaining ecological balance while providing a functional and attractive living space.