5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
The “House of the Future” is a design project situated in the United Arab Emirates, focusing on harmonizing traditional Islamic-Arabian values with contemporary architectural methods suitable for the region's climate. The intent is to create a residence that balances privacy, social interaction, and environmental sustainability, reflecting the cultural importance of hospitality in Arabian society.
### Spatial Configuration
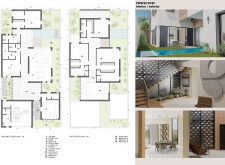
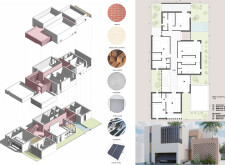
The layout employs a modular approach, consisting of interconnected volumes that optimize both functionality and aesthetic cohesion. Key spaces include an "Al Majlis," a traditional gathering area acting as a transitional zone between public and private realms. The spatial arrangement delineates distinct modules for communal living—such as the living room, dining area, and kitchen—while reserving private zones including bedrooms and an office. The design promotes interaction in communal areas while ensuring discreetness in personal spaces. The ground floor facilitates easy access to outdoor environments, while the first floor incorporates a void that enhances light and air circulation throughout the house.
### Materiality and Sustainability
Material selection in the design is carefully considered to achieve durability and thermal efficiency. Key components include structural and decorative bricks, palm wood for interior finishes, and concrete utilized in load-bearing elements. The inclusion of tinted glass enhances privacy while allowing natural light, complemented by aluminum fixtures for a contemporary touch. Solar panels contribute to energy efficiency, underscoring an emphasis on sustainability. Passive cooling strategies—such as natural ventilation and solar shading—are integrated to reduce reliance on mechanical cooling systems, aligning with environmentally responsible architectural practices. The design reflects a commitment to both ecological sustainability and the quality of life for its occupants.