5 key facts about this project
## Overview
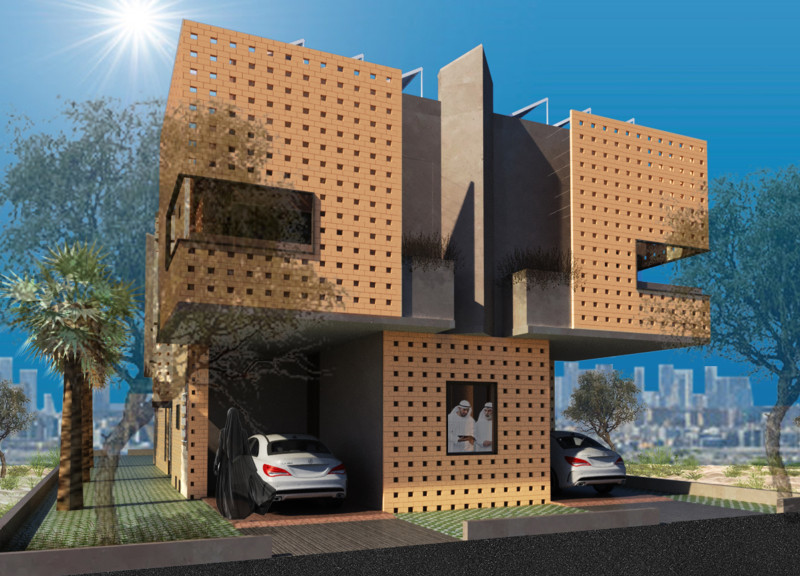
The Solar Filter project is situated in an arid climate and exemplifies a commitment to sustainable architectural design. Its intent is to effectively integrate natural materials with energy-efficient strategies, establishing a balance between the built environment and its natural surroundings. This multi-faceted approach addresses environmental challenges while reflecting traditional vernacular architecture's response to local contexts.
## Spatial Strategy
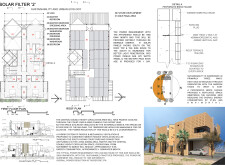
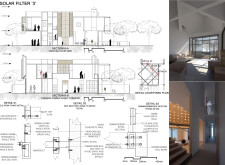
A thoughtful spatial organization delineates public and private areas, enhancing both community interaction and individual privacy. The incorporation of courtyards and private gardens is particularly beneficial in catering to cultural sensitivities, fostering a sense of belonging for residents. This layout not only satisfies functional requirements but also creates opportunities for outdoor engagement, encouraging social cohesion.
## Materiality and Energy Efficiency
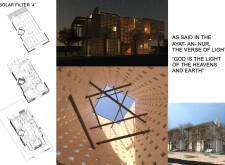
The predominant construction material is recycled brick aggregate, utilized to construct perforated walls that promote passive ventilation essential for hot climates. Reinforced concrete serves as a structural backbone, ensuring stability while allowing for innovative design features, such as light filtering. Solar panels are integrated into the design to maximize energy capture. The project showcases a notable reduction of 37% in monthly energy consumption, reflecting a balance of aesthetic appeal and environmental responsibility through the dynamic interplay of light and shadow created by the facade.