5 key facts about this project
## Overview
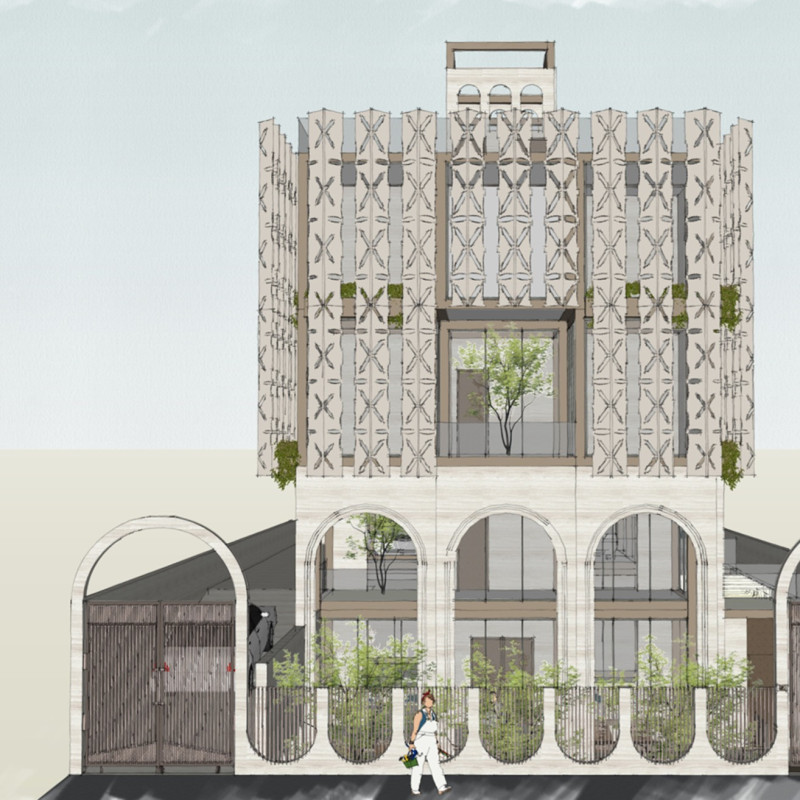
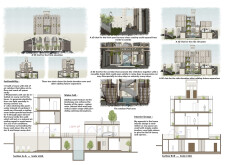
The House of the Future is situated on a 15 by 30 meter plot in Dubai, designed to respond to the region's contemporary living demands and environmental challenges. The project maximizes the building footprint while ensuring privacy and functionality amid a dense urban setting. The layout embraces optimal air circulation and natural light, addressing the extreme climate prevalent in the area.
## Design Strategy and Functionality
### Modular Design for Flexibility
The design utilizes a modular, prefabricated approach that emphasizes sustainability. A basement is incorporated to separate service functions from the primary living areas, allowing for a more organized circulation path. This division enhances accessibility and optimizes space usage. The modular steel framework stands atop a concrete foundation, facilitating streamlined construction while reinforcing structural integrity.
### Integrated Sustainable Features
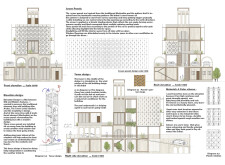
Sustainability is a priority in the design, with features such as passive cooling strategies, advanced water management systems, and photovoltaic panels for energy generation. A central wind tower serves as a natural ventilation system, channeling breeze into living spaces to reduce reliance on mechanical cooling methods.
## Material Selection and Aesthetic
The project employs a selection of durable materials that effectively balance functionality with aesthetic appeal. Concrete forms the foundation for stability, while a prefabricated steel framework offers resilience and quick assembly. Travertine stone clads the exterior, combining luxury with thermal performance. Photovoltaic panels are strategically positioned to leverage Dubai's sunlight, enhancing energy efficiency. The warm color palette is designed to create inviting interior environments, reinforcing a family-oriented atmosphere.
### Spatial Organization and Connectivity
The interior layout promotes an open-concept design that merges living, dining, and kitchen areas, supported by large windows that facilitate natural light penetration. The Majlis room, located within the service volume, respects cultural norms of hospitality while maintaining accessibility for residents and guests. Vertical connectivity is achieved through a panoramic elevator and generous terraces, fostering interaction between different levels and outdoor spaces.
Circulation pathways are clearly defined, improving navigation throughout the house. Entrances are designed for ease of access, accommodating both residents and visitors, and thereby enhancing the building’s overall functionality.