5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
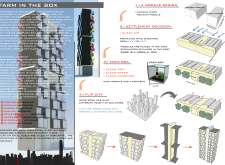
"Farm in the Box" is a modular housing initiative located in Hong Kong, an urban area characterized by high population density, humidity, and limited land availability for construction. The project seeks to address urban living challenges through innovative architectural solutions that emphasize sustainability, adaptability, and community engagement within residential environments.
## Modular Housing and Community Spaces
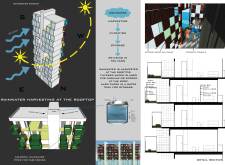
The design centers on modular units, offering flexibility with single modules measuring 15 m² and double modules at 30 m². This adaptability allows for various configurations to meet the diverse needs of residents. Each unit is strategically oriented to maximize natural light and ventilation, enhancing the living experience. Integral to the design is the incorporation of "Farm Boxes," designated areas for urban agriculture that support food security and encourage residents to grow their own produce. The utilization of rainwater harvesting systems further emphasizes sustainability, providing a reliable water source for these farming spaces.
Ground-floor retail areas promote local business developments and act as communal hubs, fostering social interaction and a vibrant community atmosphere. Semi-public spaces within the design facilitate connections among residents, reinforcing a sense of belonging in a densely populated context.
## Materiality and Sustainability Measures
The selection of construction materials aligns with the project's sustainability objectives. Steel is employed for structural elements, ensuring durability and flexibility, while concrete provides necessary stability. Glass façades enhance natural light entry and outdoor connectivity, and wood is utilized in shading elements to improve thermal comfort and aesthetics. Epoxy flooring contributes to long-term durability and maintenance ease, while soil in the farm boxes supports organic farming initiatives.
The overall design showcases dynamic aesthetics through the colorful arrangement of farm boxes, creating a visually distinct identity amidst typical urban structures. The project prioritizes natural ventilation and climate control, contributing to indoor comfort and reducing dependence on artificial cooling systems, solidifying its role as a model for sustainable urban living.