5 key facts about this project
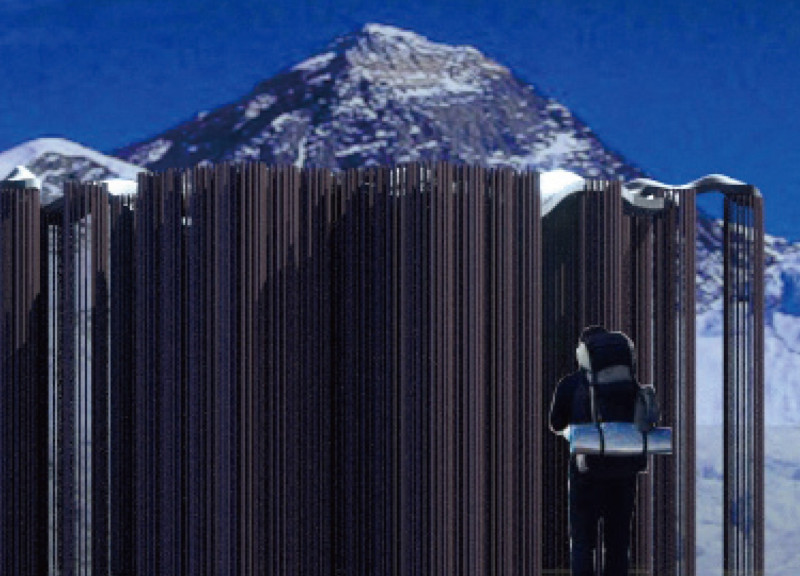
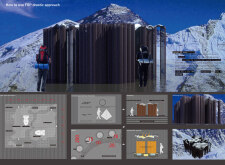
At its core, the project serves a multifaceted function. It provides essential shelter that meets contemporary living standards while also engaging with the natural environment. The use of FRP not only ensures durability against harsh weather conditions but also minimizes the building's overall footprint, which is vital in such a sensitive ecological area. The architecture promotes both individual privacy and community interaction, establishing a harmonious balance of social and personal spaces within the structure.
The design embodies several important components that contribute to its uniqueness. The structure’s form, characterized by vertical elements arranged in parallel, signifies strength and resilience. This sleek profile is purposeful in responding to lateral forces prevalent in high-altitude settings, where high winds can pose significant challenges. Additionally, the choice of lightweight materials like FRP reduces the load on the foundation, facilitating easier assembly and minimizing site disruption.
An essential aspect of this architectural project is its emphasis on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. The design incorporates features such as thermal insulation panels and water-resistant coatings, further enhancing the building's performance in extreme climates. Features like large windows are strategically placed to maximize natural light and breathtaking views of the surrounding mountains, promoting a connection between the inhabitants and the landscape. Through these elements, the architecture defines a space that is not only functional but also sensitive to its environment.
Particularly noteworthy is the adaptability of the project. By leveraging FRP, the design enables modularity, allowing it to be deployed in various configurations tailored to different contexts without compromising its structural integrity. This adaptability is a fundamental consideration for architecture in remote areas, where logistical challenges can complicate traditional construction methods.
Moreover, the project’s approach to integrating advanced materials paves the way for a broader discussion on sustainable building practices. FRP as a primary material makes a compelling case for modern architecture, encouraging industry professionals to reassess conventional building materials in favor of options that promote efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Readers interested in a comprehensive understanding of this architectural design are encouraged to explore the project presentation, which includes detailed architectural plans, sections, and designs. These elements provide insight into the innovative approaches employed, as well as the overall architectural ideas driving the project forward. By examining these aspects, one can appreciate how this project not only champions contemporary architectural practices but also sets a potential precedent for future endeavors in similar challenging environments.