5 key facts about this project
## Overview
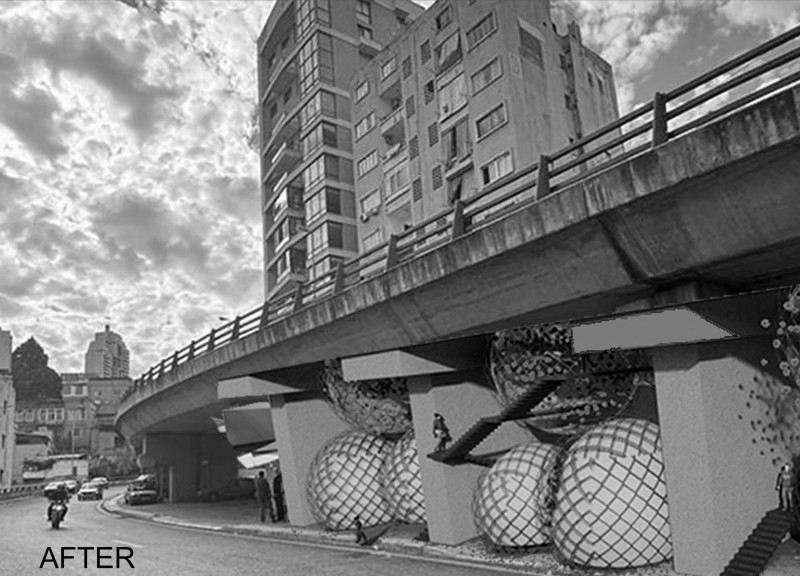
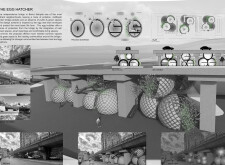
"The Egg Hatcher" is an architectural project situated beneath one of Beirut's independence bridges, aimed at revitalizing an underutilized and polluted urban space into a community-oriented environment. The design approach addresses environmental degradation while fostering social interaction, reflecting an intent to enhance the quality of life for local residents through the thoughtful integration of architecture and nature.
## Spatial Strategy and Integration
The design employs egg-shaped structures, designated as "Egg Bubbles," which function as both ecological hatches and community hubs. These spherical formations feature a lattice shell that facilitates natural light penetration while promoting biodiversity. Strategic openings within the structures create connections to the surrounding environment, enhancing airflow and user comfort. The project also engages with the existing infrastructure of the bridge, ensuring that the design aligns with its verticality and utility, turning a marginalized area into an active civic space.
## Materiality and Environmental Considerations
The selection of materials is critical to the project's functionality and identity. Glass is employed in the lattice structures to allow for transparency and light, while concrete serves as the primary material for durability and structural integrity, supporting the weight of the overhead bridge. Steel reinforces the overall design, providing necessary strength and flexibility. Additionally, natural planting is integrated throughout the site, enhancing biodiversity and contributing to aesthetic appeal while helping to mitigate pollution and improve micro-climates. This focus on materiality underscores the commitment to sustainability and ecological resilience within the urban context.