5 key facts about this project
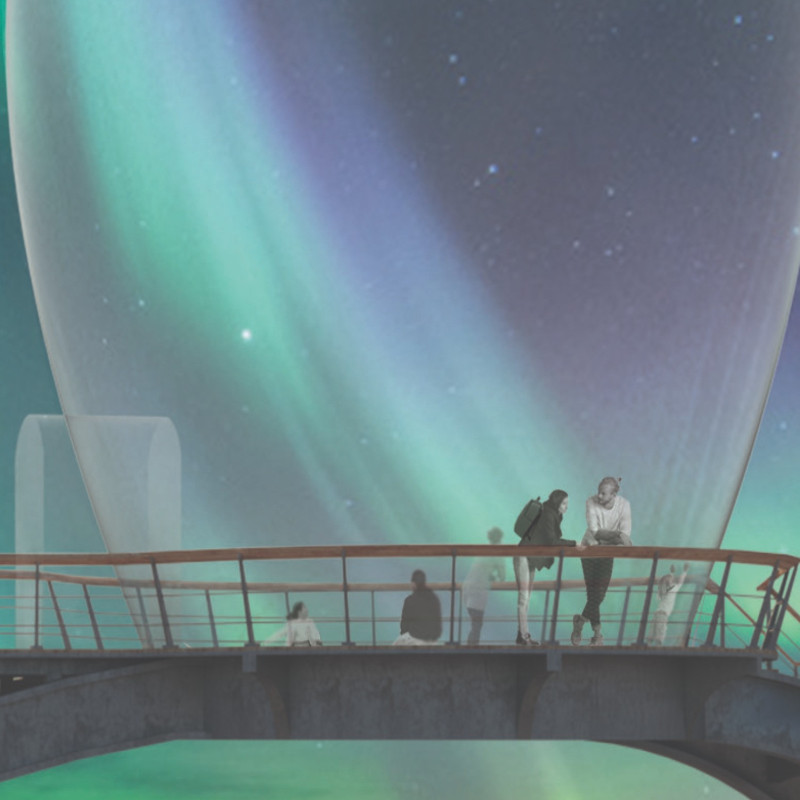
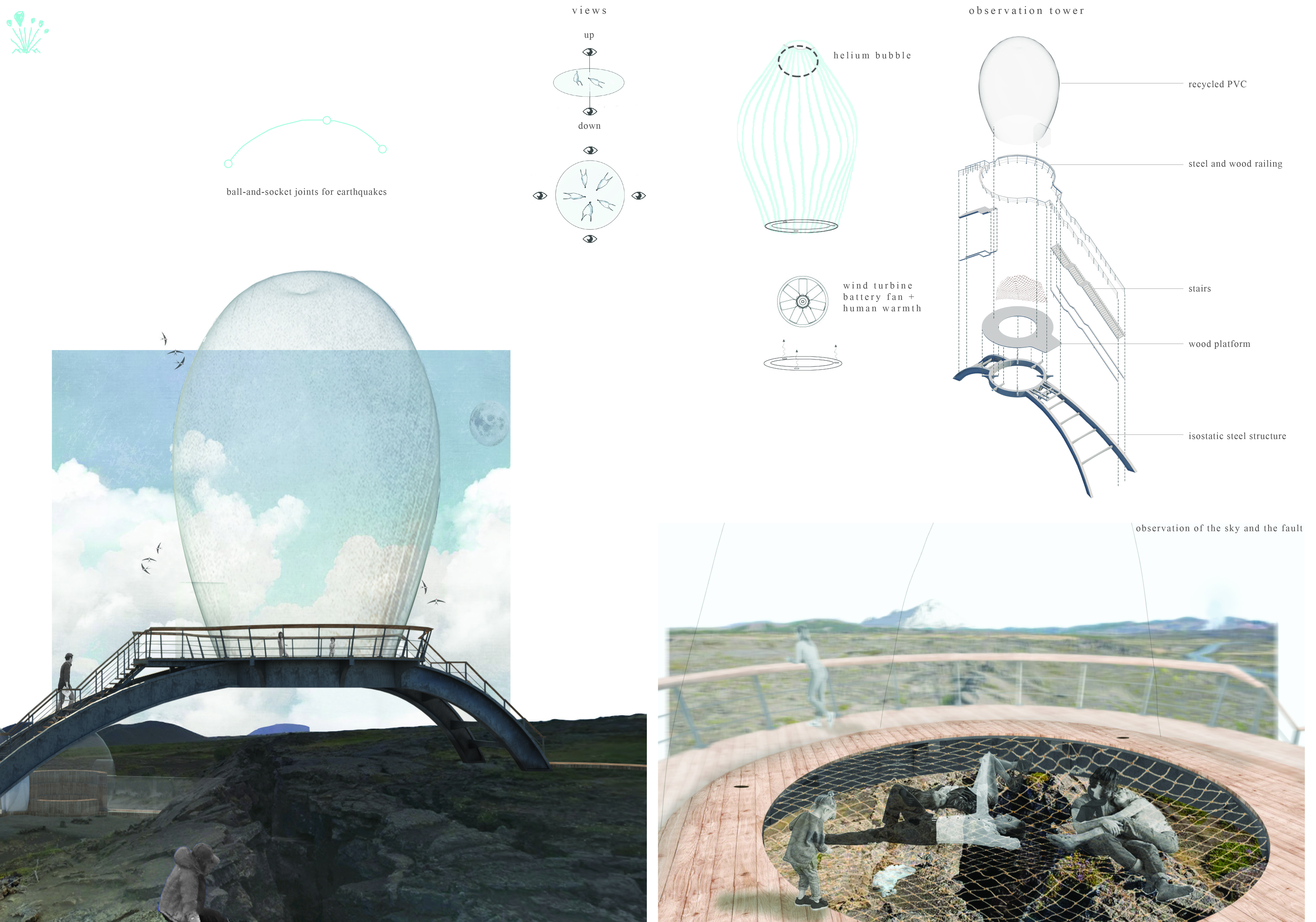
The primary function of the Grjótajgá observation balloon is to serve as a viewpoint for visitors seeking to appreciate the natural beauty of Iceland. By elevating its users above the rugged terrain, the structure allows for unobstructed views of the night sky, creating a perfectly positioned vantage point from which the celestial display can be enjoyed. In addition to its observational role, the project also incorporates educational elements about the local geology, particularly the fascinating tectonic activities that characterize Iceland.
The design of the observation balloon incorporates several essential components that contribute to both its functionality and overall aesthetic. A standout feature of the structure is its inflatable envelopes, which are constructed using recycled PVC. These elements define the outer shell of the balloon, providing a lightweight and flexible facade that allows easy transportation and setup. This approach to materiality not only minimizes environmental impact but also reflects a commitment to sustainability, a core value of contemporary architecture.
The observation balloon also includes multiple viewing decks designed to facilitate a safe and comfortable experience for visitors. These decks are constructed from a robust metallic material, ensuring durability in the face of Iceland's often harsh weather conditions. In an effort to enhance user experience, the interior spaces are carefully planned to allow for smooth flow and accessibility, accommodating various visitor needs.
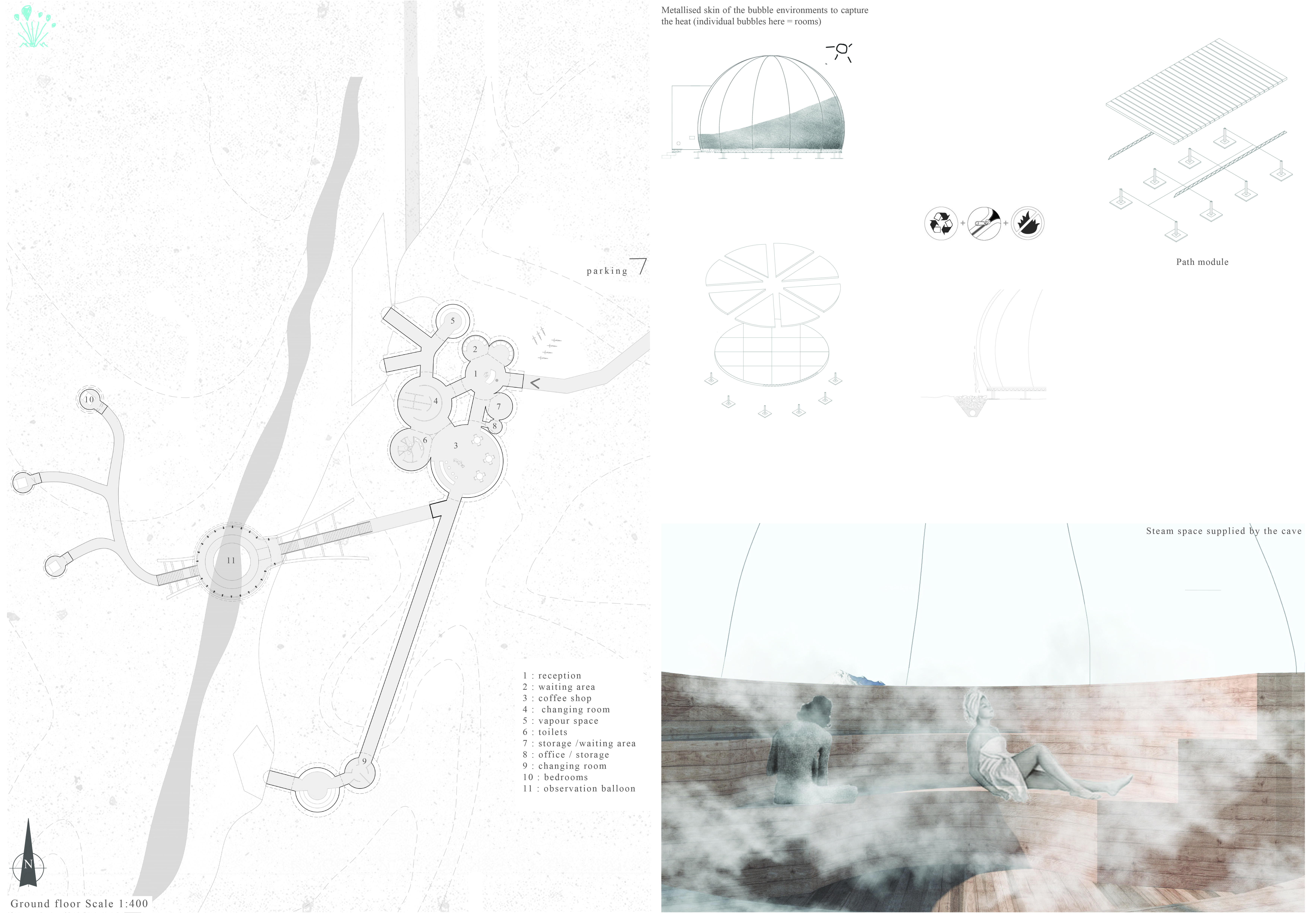
Key architectural elements extend beyond the structure itself. Features such as a reception area, complete with facilities for visitors, and amenities like changing rooms and a sauna leverage Iceland's geothermal energy, further merging the project with its natural context. This holistic approach to design underscores the project’s ethos of integrating architectural solutions with ecological considerations.
The idea of merging an interactive structure with a natural environment sets this project apart in contemporary architectural discourse. Grjótajgá incorporates sustainable systems, including wind turbine technologies that harness renewable energy without detracting from the surrounding landscape. These features not only provide power to the facility but also emphasize the importance of environmental stewardship within modern architectural practices.
Visitors are invited to engage fully with their surroundings, creating memorable experiences that foster a connection with both the land and the skies above. The structure becomes more than just a building; it transforms into a destination where people can appreciate the natural world, learn about geological phenomena, and enjoy communal activities in a thoughtfully designed space.
Grjótajgá serves as a notable example of how architecture can respond to its environment both thoughtfully and innovatively. Its design reflects contemporary ideas about sustainability, purpose, and the potential for structures to enhance our interactions with nature. For those interested in exploring this architectural project further, the presentation of the Grjótajgá observation balloon offers detailed insights into its architectural plans, sections, and design elements that underscore the unique ideas and philosophies behind the project. Readers are encouraged to delve deeper to fully appreciate the intricacies of this architectural achievement.