5 key facts about this project
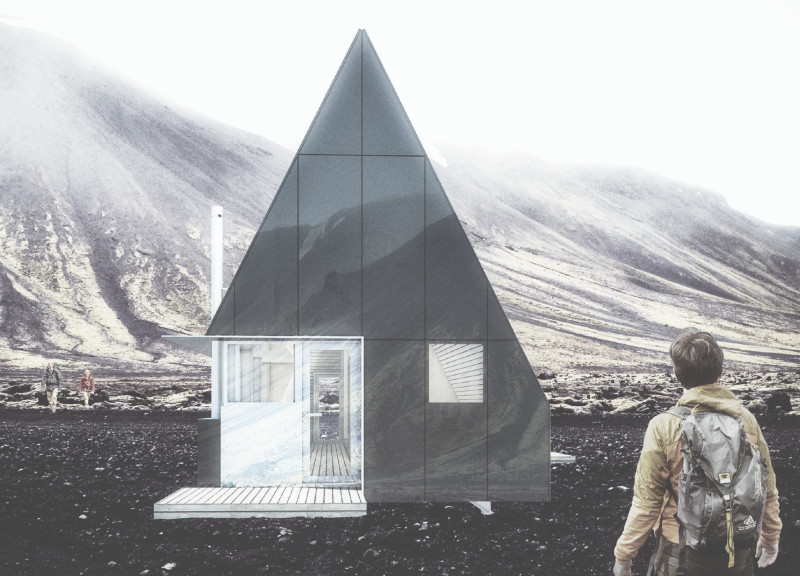
The architecture of the Shadow Hut is fundamentally rooted in the principles of sustainability and minimalism. The structure is a modest yet efficient solution to provide shelter, warmth, and community space without imposing on its surroundings. Constructed with durable materials that withstand Iceland's climatic challenges, the hut emphasizes resilience. The exterior is clad in reflective black solar panels, allowing it to merge seamlessly with the rocky landscape while harnessing solar energy. This careful material selection extends to other aspects of the design, including treated wood for the internal structure, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and structural stability.
Functionally, the Shadow Hut is divided into distinct modules, each serving a specific purpose—such as sleeping quarters, communal cooking areas, and storage spaces. This modular approach not only allows for flexibility and ease of transport but also promotes an efficient use of space, ensuring visitors can comfortably enjoy their stay. The design encourages social interaction among occupants, fostering a sense of community, which is essential during extended outdoor excursions.
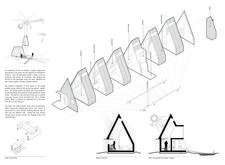
A unique aspect of the design process includes the architectural form that draws inspiration from traditional Icelandic buildings, such as turf houses and Scandinavian A-frames. The steeply pitched roof is a practical response to the needs of the surrounding environment, facilitating snow runoff and maximizing interior space. The strategic placement of large windows invites natural light into the interior while framing picturesque views of the Icelandic landscape. This integration of light and space creates an inviting atmosphere, making the interior feel both expansive and cozy.
The architectural design also employs biophilic principles, aiming to strengthen the connection between the inhabitants and the environment. By using sightlines that connect the interior with the exterior landscape, the hut enhances the occupants’ experience of nature, encouraging a deeper appreciation for the beauty surrounding them. The use of skylights allows natural light to flood the space, creating dynamic changes throughout the day as the sun moves across the sky.
Furthermore, the sustainable features of the Shadow Hut include a rainwater collection system and provisions for geothermal energy, which underscore a commitment to environmental stewardship. These design choices are indicative of a broader architectural trend focused on reducing ecological footprints while enhancing the user experience. The self-sufficient energy and water systems allow the hut to function independently, making it a responsible choice for outdoor enthusiasts concerned about their impact on the environment.
In analyzing the Shadow Hut project, it becomes clear that it is not merely a shelter; it is a well-considered architectural response to the challenges posed by its environment. The design addresses practical needs while also preserving the cultural heritage of Icelandic architecture and encouraging social interaction among users. Each element, from the structure’s materials to its layout, has been thoughtfully curated to align with both the natural and cultural landscapes.
For those interested in exploring the intricacies of this project, reviewing the architectural plans, sections, and designs will provide deeper insights into the thoughtful considerations that have gone into creating this unique structure. Whether it's the innovative approach to materiality, the sustainable energy solutions, or the design principles underlying the layout, there is much to discover in the Shadow Hut's architectural narrative.