5 key facts about this project
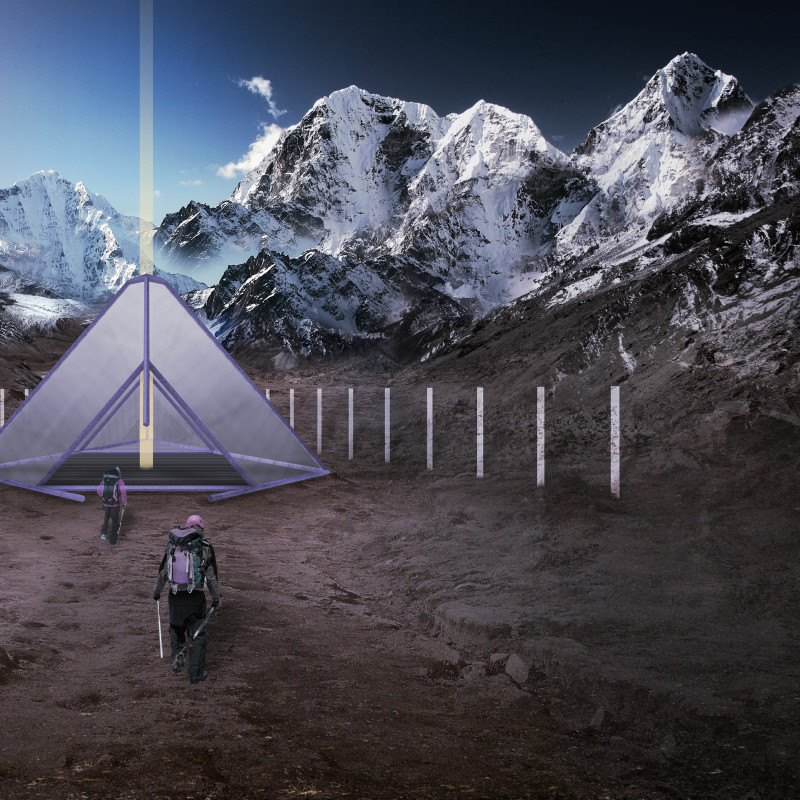
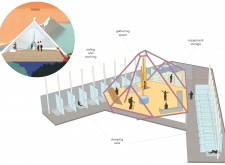
At its core, this project functions as a shelter for climbers and trekkers, providing not just a safe haven from the harsh weather conditions but also a space for social interaction and community engagement. The design centers around a circular layout, reminiscent of a mandala, which encourages gathering and collaboration among visitors. This design approach emphasizes the importance of shared experiences in the isolated setting of the mountains, fostering a sense of unity and collective endeavor.
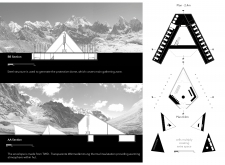
The major architectural elements of the Bindu 4600 include a pyramid-like structure, which is not only visually appealing but also practical in handling the extreme weather conditions prominent in the Himalayas. The form maximizes internal space and offers structural stability against high winds and heavy snowfall. Inside, the layout is carefully organized into distinct functional zones, including social gathering areas and secluded sleeping units. This thoughtful arrangement ensures that communal and private needs coexist harmoniously, allowing individuals to recharge while remaining part of a collective atmosphere.
One of the most significant aspects of this architectural design is its emphasis on sustainability. The materials selected for the project have been chosen for their durability and energy efficiency. The steel structure serves as the backbone of the hut, facilitating a sturdy, protective dome that shields visitors from the elements. The use of TWD (Transparente Wärmedämmung) thermal insulation helps retain internal warmth while allowing natural light to permeate the space. Additionally, LightPanels are integrated on the hut's exterior, transforming sunlight into usable energy and further enhancing the overall sustainability of the design.
Water management is another critical consideration in the Bindu 4600 project. The design includes specific systems for atmospheric water collection and filtration, ensuring that visitors have access to clean water even in this remote location. This attention to detail illustrates how architecture can not only provide shelter but also cultivate a responsible relationship with the surrounding environment.
The architectural designs of the Bindu 4600 also prioritize user well-being through elements such as the incorporation of glass tubes for natural light and oxygen in sleeping units. This approach effectively improves the living conditions for occupants, creating a healthier indoor environment that supports both physical and mental well-being.
In conclusion, the Himalayan Mountain Hut Bindu 4600 exemplifies how architecture can address both immediate functional needs and broader communal aspirations in challenging environments. It offers a unique blend of contemporary design, sustainable practices, and a deep respect for the traditional values of community living among mountaineers. Those interested in architectural plans, sections, and diverse architectural designs are encouraged to explore the project presentation further to gain deeper insights into its unique features and the innovative ideas that shapes its function and representation in the rugged beauty of the Himalayas.